This promotional material is intended for UK Healthcare Professionals only.
BOTOX® (botulinum toxin type A) Prescribing Information and adverse event reporting information can be found below.
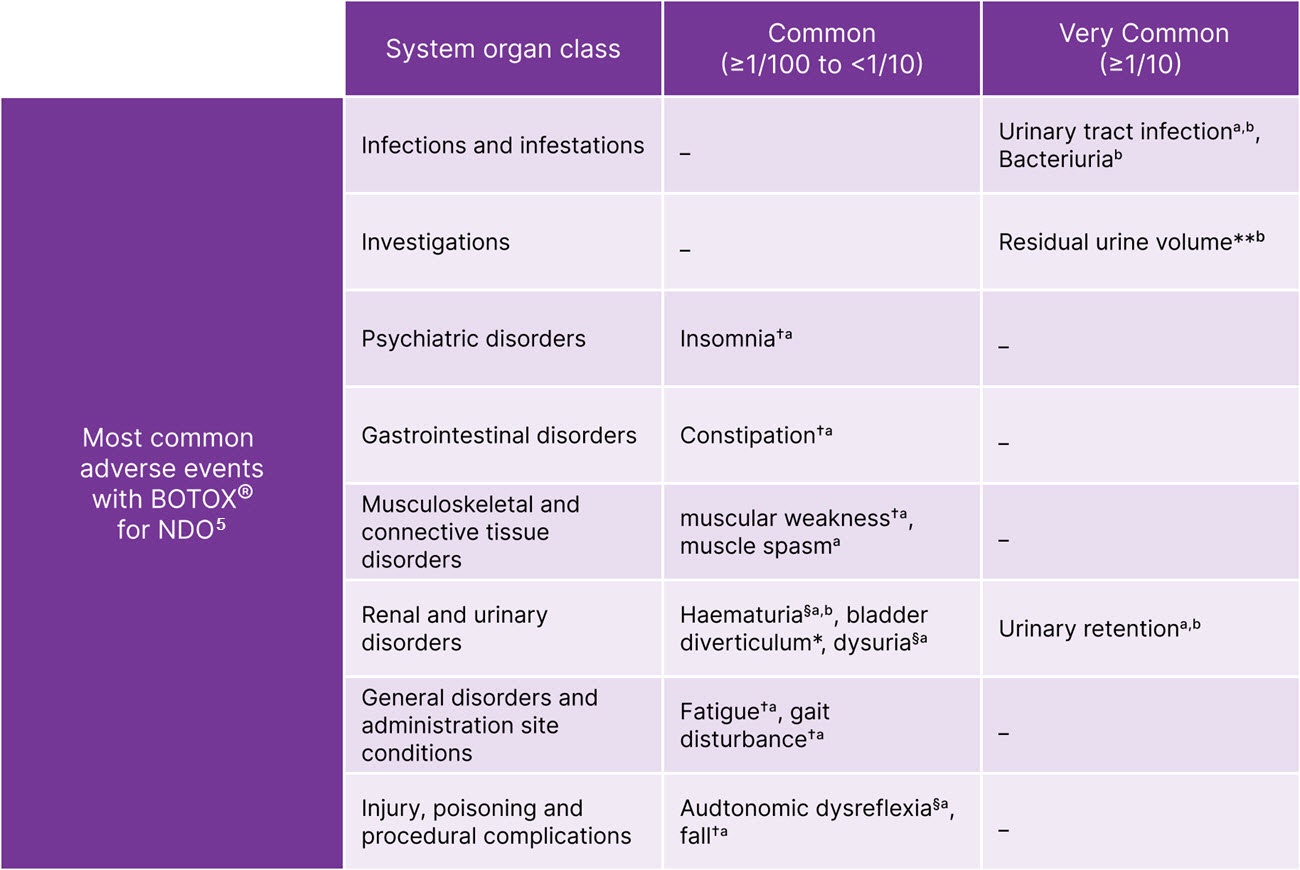
BOTOX® has safety and tolerability experience from +30 years of use in a range of conditions5-7
BOTOX® is generally well-tolerated in NDO5
Adapted from BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics.5
§Procedure-related adverse reactions. **Elevated PVR not requiring catheterisation. †Only in multiple sclerosis. aAdverse reactions occurring in the Phase 2 and pivotal Phase 3 clinical trials. bAdverse reactions occurring in the post-approval study of BOTOX® 100U in MS patients not catheterising at baseline. Please note, BOTOX® 100U is not licensed for NDO.
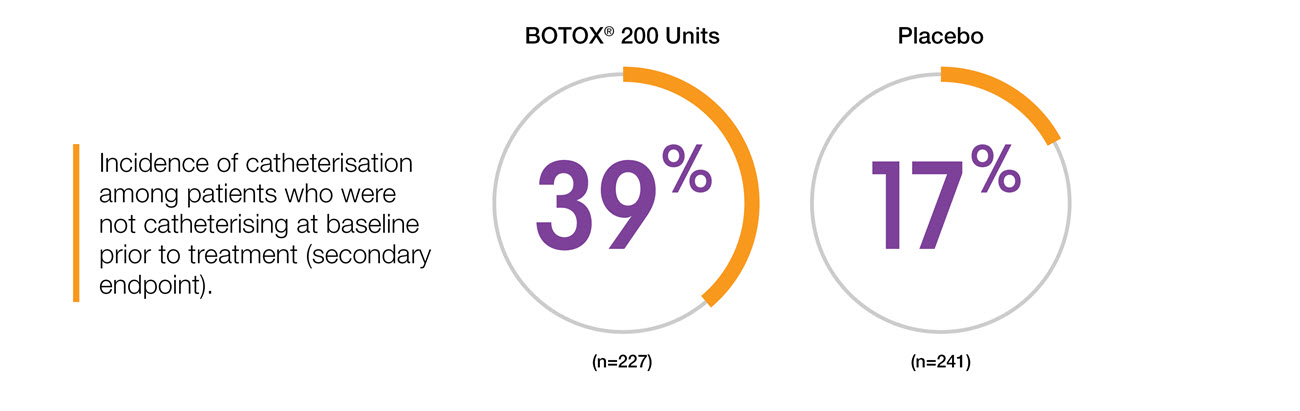
Clean intermittent catheterisation (CIC) rates in NDO5
Adapted from BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics.5
Study context: Two double-blind, placebo controlled, randomised phase 3 clinical studies, in 691 patients with urinary incontinence due to NDO. To compare the change in baseline for BOTOX® versus placebo. The primary endpoint was the mean change at week 6 in weekly frequency of urinary incontinence.5
CIC rates are higher in NDO than OAB5, however QoL was still improved in de novo catheterisers8
 BOTOX® in NDO: Urinary retention 17% BOTOX® (n=227) vs 3% placebo (n=241)5
BOTOX® in NDO: Urinary retention 17% BOTOX® (n=227) vs 3% placebo (n=241)5
 MS – 29% BOTOX® vs 4% placebo5; SCI – 5% BOTOX® vs 1% placebo5
MS – 29% BOTOX® vs 4% placebo5; SCI – 5% BOTOX® vs 1% placebo5
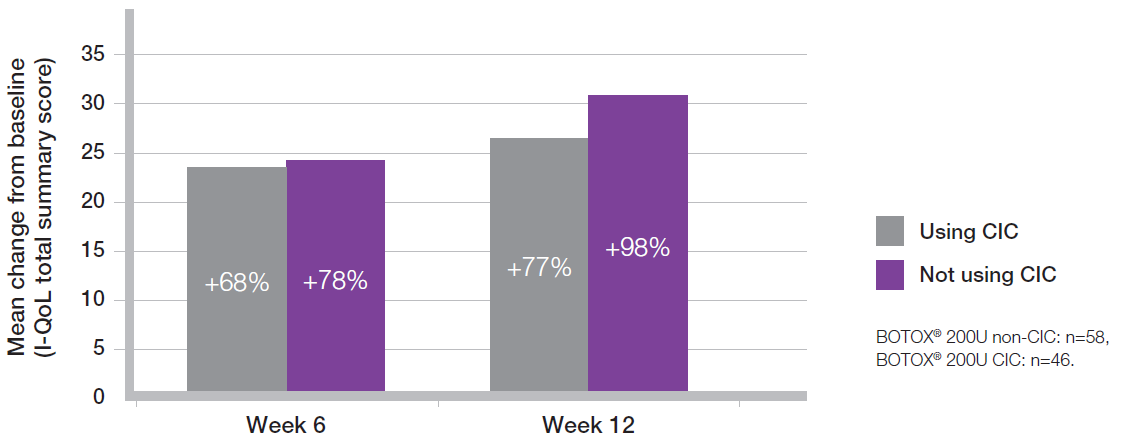
QoL scores improved with BOTOX® regardless of whether patients needed to CIC or not8
Adapted from Allergan Ltd. Data on File 0408
Study context: The pooled results of two multicenter, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel group phase 3 clinical studies, in 142 patients with urinary incontinence due to NDO, to compare the safety and efficacy of BOTOX® versus placebo. The primary endpoint for both studies was the number of weekly episodes of urinary incontinence.8
Mean baseline scores: BOTOX® 200U non-CIC 31.33, BOTOX® 200U CIC 34.85.
CIC: clean intermittent catheterisation; I-QoL: incontinence quality of life; MS: multiple sclerosis; NDO: neurogenic detrusor overactivity; OAB: overactive bladder; QoL: quality of life; SCI: spinal cord injury; UI: urinary incontinence.
Please refer to the BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics for further information on adverse events, contraindications and special warnings and precautions for use. The BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics can be found here
By clicking the link above you will leave the AbbVie Pro website and be taken to the eMC PI portal website.
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at https://yellowcard.mhra.gov.uk/
Adverse events should also be reported to AbbVie on GBPV@abbvie.com
Date of preparation: June 2025. UK-BUO-250046.