This promotional material is intended for UK Healthcare Professionals only.
BOTOX® (botulinum toxin type A) Prescribing Information and adverse event reporting information can be found below.
Reduce the impact of neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) on your patients' lives
BOTOX®: significant and sustained improvements for NDO patients5,6,7
Reduce the impact of NDO symptoms on your patients’ lives.
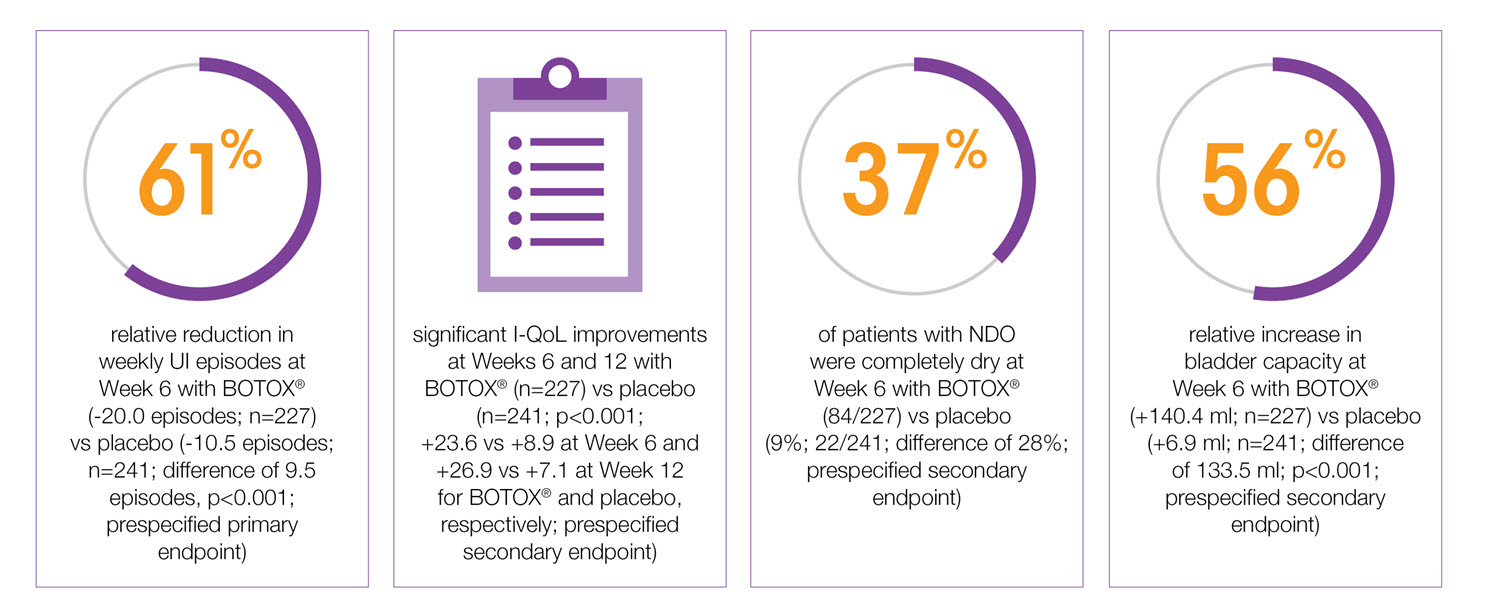
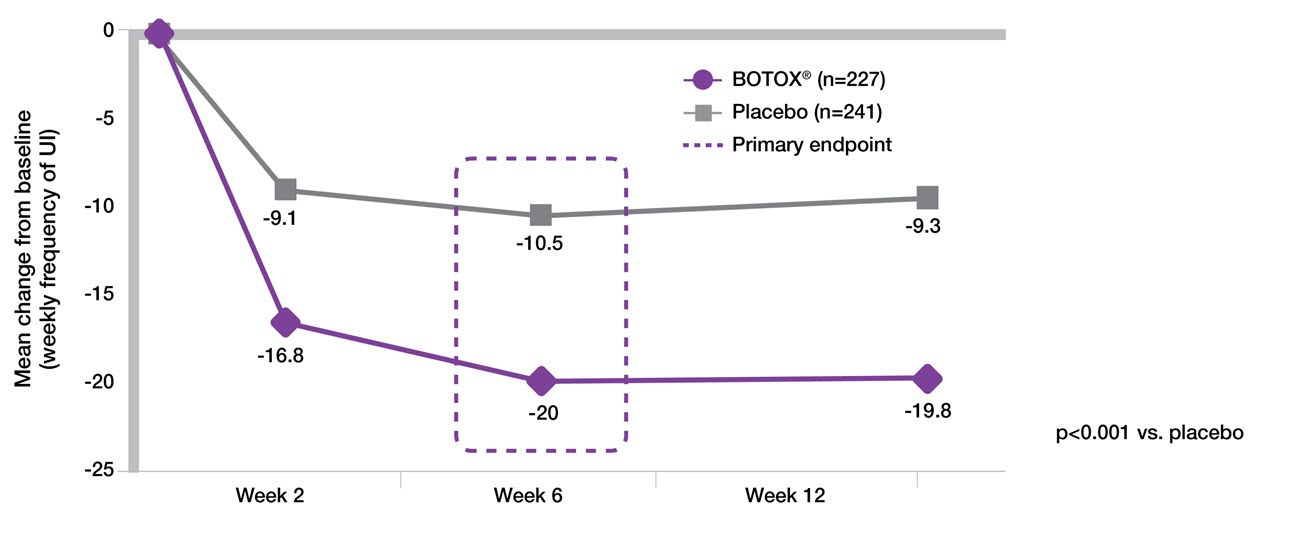
Study context: Pooled analysis of two double-blind, placebo controlled, randomised phase 3 clinical studies, in 691 patients with urinary incontinence due to NDO. To assess the efficacy, safety and effects on quality of life of BOTOX® patients with NDO. Mean baseline weekly frequency of UI: 32.4 BOTOX® and 31.5 Placebo.5
BOTOX® 200 U provides 61% reduction in UI episodes from a single treatment at week 65-7
Adapted from BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics.5
Study context: Two double-blind, placebo controlled, randomised phase 3 clinical studies, in 691 patients with urinary incontinence due to NDO. BOTOX®: n=227, placebo: n=241. Baseline weekly frequency of UI: BOTOX® 200U 32.4, placebo 31.5.5
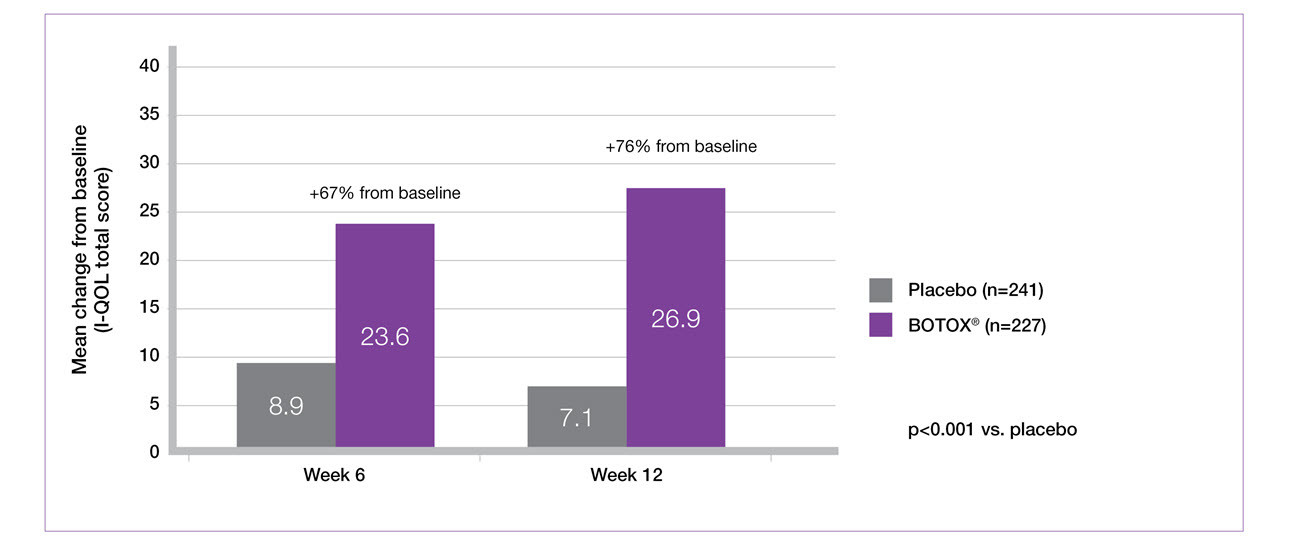
BOTOX® 200U demonstrates significant I-QOL improvements at weeks 6 and 12 versus placebo (secondary endpoint)5-7
Adapted from BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics.5
Study context: Two double-blind, placebo controlled, randomised phase 3 clinical studies, in 691 patients with urinary incontinence due to NDO. BOTOX® 200U: n=227, placebo: n=241. Mean baseline I-QoL scores: BOTOX® 200U 35.4, placebo 35.3.5
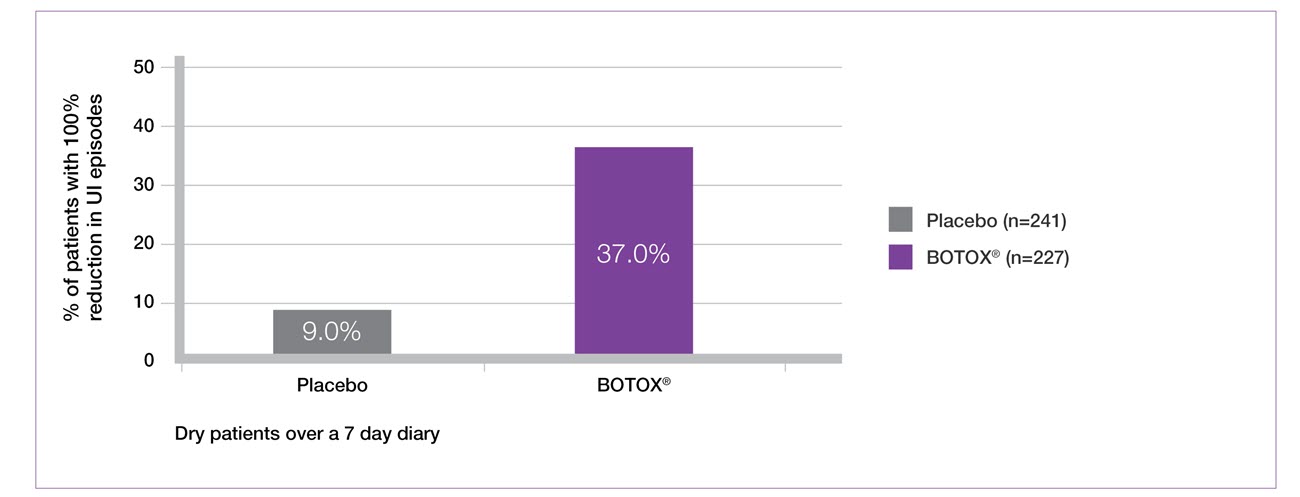
37% of patients were dry by week 6 with BOTOX® 200 U (secondary endpoint)5-7
Adapted from BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics.5
Study context: Two double-blind, placebo controlled, randomised phase 3 clinical studies, in 691 patients with urinary incontinence due to NDO. Results at Week 6. BOTOX® 200U: n=227, placebo: n=241. Mean baseline incontinence episodes/week: BOTOX®=32.4, placebo=31.5.5
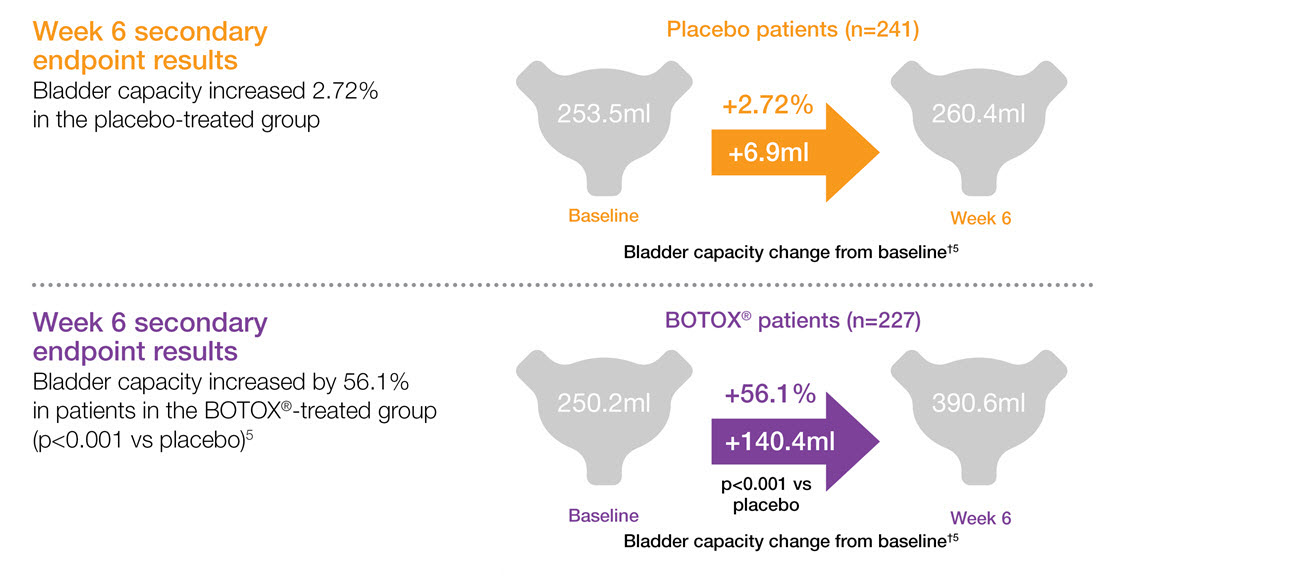
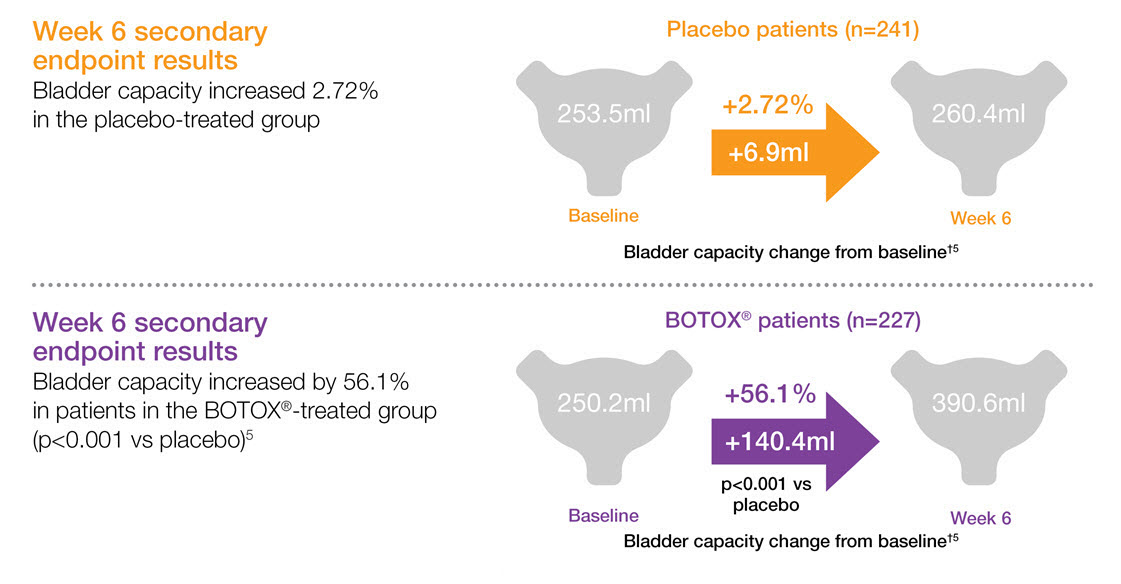
BOTOX® increases bladder capacity in patients with urinary incontinence due to NDO5,6,7
Adapted from BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics.5
Study context: Two double-blind, placebo controlled, randomised phase 3 clinical studies, in 691 patients with urinary incontinence due to NDO. Pooled pivotal study data.5
†Bladder capacity was defined as maximum cystometric capacity and is shown as mean change from baseline.
I-QoL: Incontinence-quality of life; NDO: neurogenic detrusor overactivity; UI: urinary incontinence.
Please refer to the BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics for further information on adverse events, contraindications and special warnings and precautions for use. The BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics can be found here
By clicking the link above you will leave the AbbVie Pro website and be taken to the eMC PI portal website.
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at https://yellowcard.mhra.gov.uk/
Adverse events should also be reported to AbbVie on GBPV@abbvie.com
Date of preparation: June 2025. UK-BUO-250045.