Efficacy
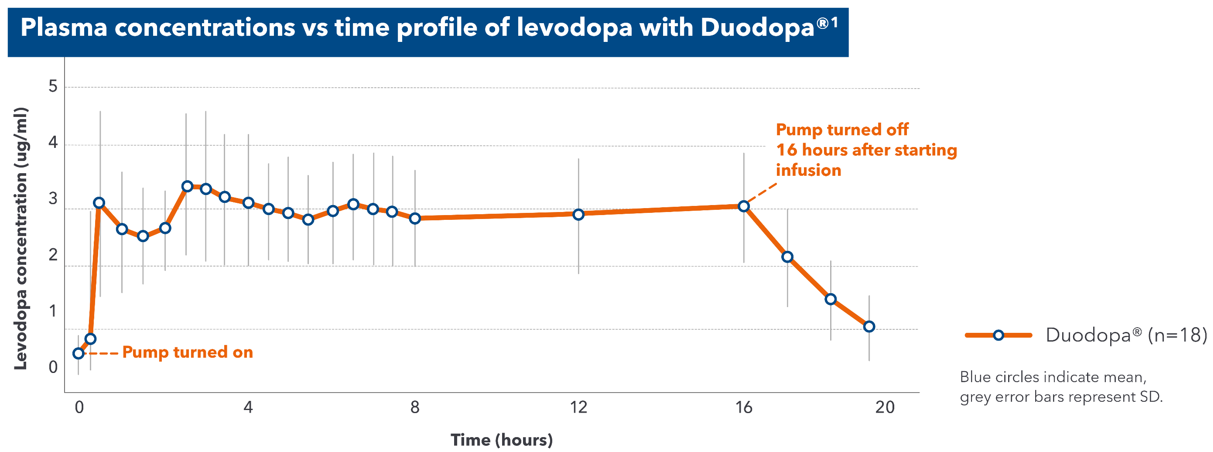
Continuous infusion of Duodopa® can provide a smooth and consistent delivery of levodopa1
- Duodopa® rapidly achieves therapeutic plasma levels of levodopa1
- Duodopa® maintains stable plasma levodopa levels over 16 hours1
- Continuous intestinal delivery with Duodopa® allows rapid absorption, avoiding fluctuations in drug delivery that result from erratic gastric emptying1,4
Adapted from Nyholm D et al. 2013.
In a multicentre, multiple-dose, open-label study of 19 subjects with advanced PD receiving Duodopa® over 30 days:1 Treatment is usually administered during the patient's awake period. If medically justified, Duodopa® may be administered for up to 24 hours4
PD=Parkinson's disease; SD=Standard deviation.
1. Nyholm D, et al. AAPS J 2013;14:316–23.
2. Fernandez HH, et al. Mov Disord 2015;30(4):500–9.
3. Freire-Alvarez E, et al. Mov Disord. 2021;36(11):2615-23.
4. Duodopa® Summary of Product Characteristics, available on www.medicines.ie.
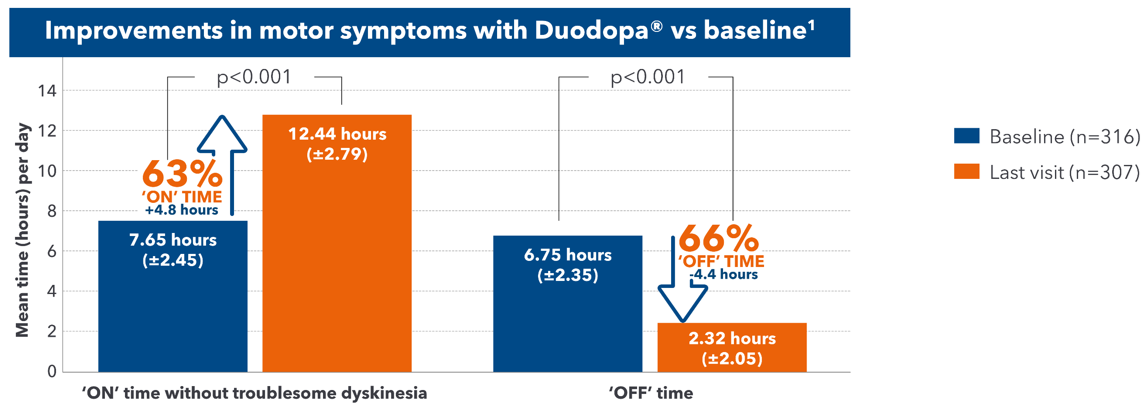
Duodopa® provides predictability of 'ON' time and 'OFF' time1
- Duodopa® has proven to provide 4.8 hours more ON time without troublesome dyskinesia compared with baseline1
- Duodopa® has proven to provide 4.4 hours less OFF time compared with baseline1
- Duodopa® showed a significant improvement in the motor symptoms of PD, sustained up to 54 weeks.1
Adapted from Fernandez HH et al. 2015.
A 54-week, international, prospective, open-label study assessed the safety and efficacy of Duodopa® in advanced PD patients with severe motor fluctuations (N=354). Safety was the primary endpoint; for the majority of patients AEs were mild or moderate and transient. Secondary endpoints included 'OFF' time, 'ON' time with/without troublesome dyskinesia, UPDRS and HRQoL outcomes.1
AE=adverse event; HRQoL=health-related quality of life; PD=Parkinson's disease; UPDRS=Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale.
1. Fernandez HH, et al. Mov Disord 2015;30(4):500-9.
- In the DYSCOVER study Duodopa® significantly improved dyskinesia compared with OMT1
- Duodopa® treatment had sustained and significant improvements in UDysRS total scores through Week 12 compared to OMT (P<0.001)1
DYSCOVER: A phase 3b, open-label, randomised, multicentre, 12-week study (N=61 ). Advanced PD patients were randomised to receive either OMT (n=33) or Duodopa® (n=28).1*
The UDysRS (Unified Dyskinesia Rating Scale) has established metric properties that can measure all aspects of dyskinesia with a comprehensive score.1
*Patients in the OMT group continued their optimised and stable anti-PD medication. Patients in the Duodopa® group discontinued all other anti-PD medications other than amantadine prior to treatment initiation on Day 1.1
OMT =optimised medical treatment; PD=Parkinson's disease; SE=standard error; UDysRS=Unified Dyskinesia Rating Scale.
1. Freire-Alvarez E, et al. Mov Disord. 2021 ;36(11):2615-23.
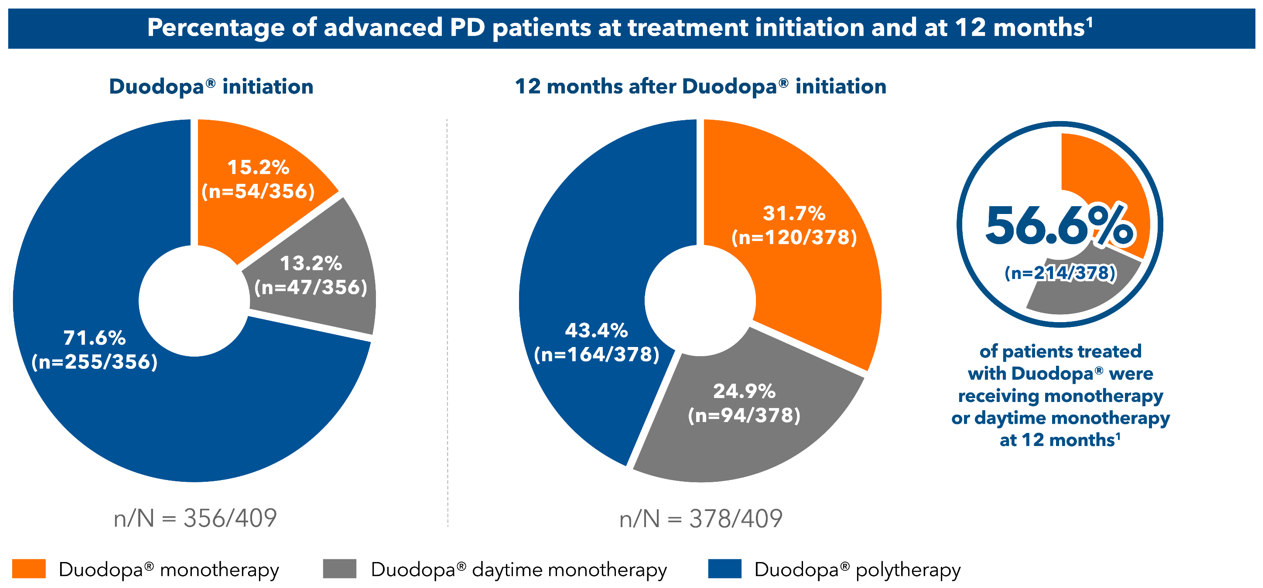
Reduced pill burden
A multi-country, retrospective, cross-sectional, post-marketing observational study of 409 advanced PD patients treated with Duodopa® for at least 12-months, investigating the effect of Duodopa® in reducing polypharmacy. The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients receiving Duodopa® monotherapy immediately after Duodopa® initiation (following PEG-J procedure) and at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after Duodopa® initiation.1
Duodopa® monotherapy=Duodopa® only with no add-on PD medications; Duodopa® daytime monotherapy=Duodopa® with add-on PD medications used in the evening after the daily infusion hours are completed; Duodopa® polytherapy=Duodopa® with add-on medications at any time.
n= patients with non-missing data.
PEG-J=percutaneous gastrojejunostomy; PD=Parkinson's disease.
1. Fasano A, et al. Mov Disord. 2021; doi: 10.1002/mds.28596.
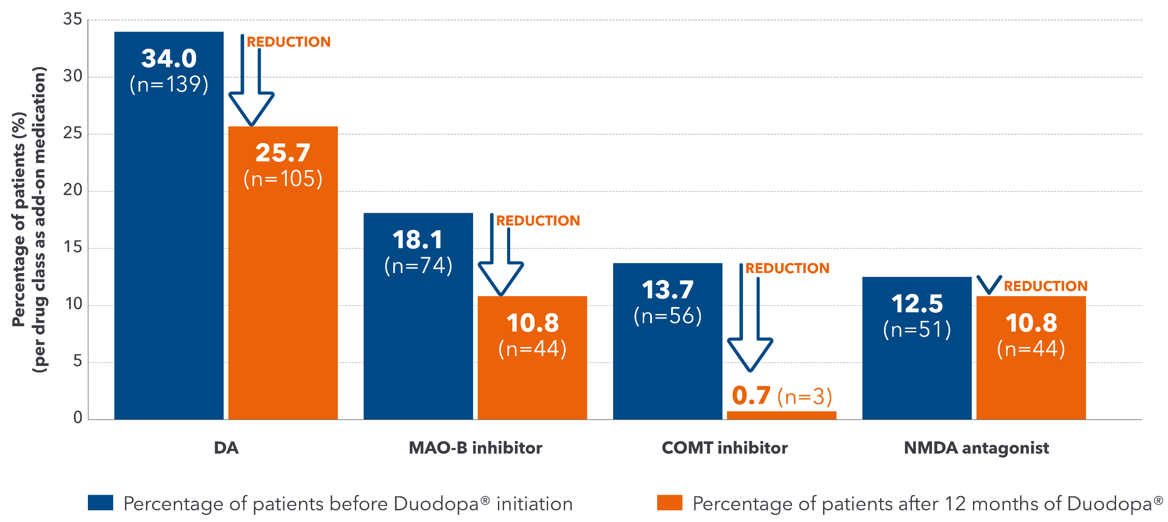
A multi-country, retrospective, cross-sectional, post-marketing observational study of 409 advanced PD patients treated with Duodopa® for at least 12-months, investigating the effect of Duodopa® in reducing polypharmacy. The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients receiving Duodopa® monotherapy immediately after Duodopa® initiation (following PEG-J procedure) and at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after Duodopa® initiation.1
COMT =catechol-O-methyl transferase; DA=dopamine agonist; MAO-B=monoamine oxidase-B; NMDA=N-methyl-D-aspartate; PD=Parkinson's disease; PEG-J=percutaneous gastrojejunostomy.
1. Fasano A, et al. Mov Disord. 2021; doi: 10.1002/mds.28596.
IE-DUOD-220032. Date of preparation: November 2022.