This promotional material is intended for UK Healthcare Professionals only.
BOTOX® (botulinum toxin type A) Prescribing Information and adverse event reporting information can be found below.
Reduce the impact of overactive bladder (OAB) on your patients' lives
BOTOX® demonstrates significant and sustained improvements for overactive bladder patients5-7
Week 12 co-primary endpoint results:
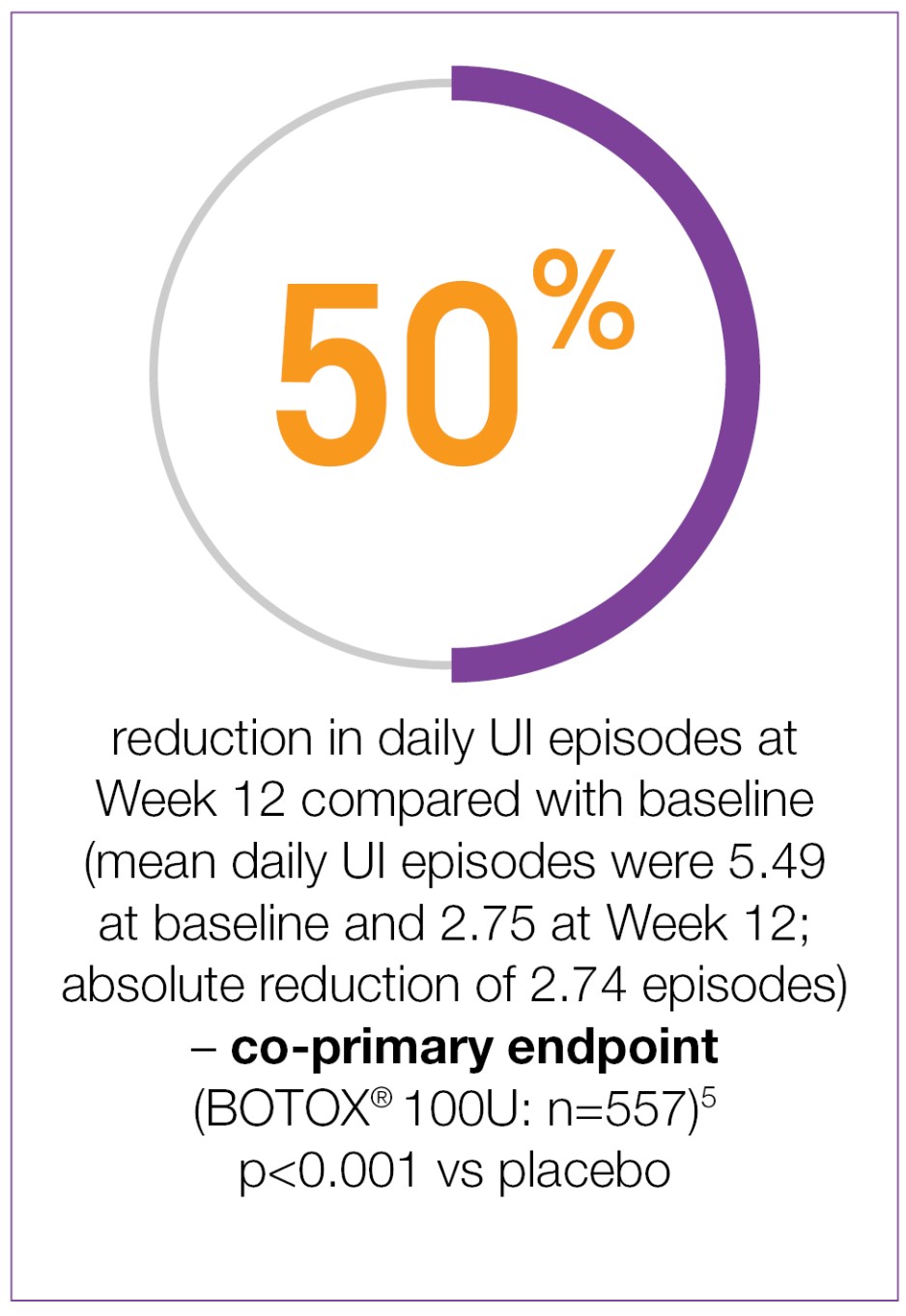
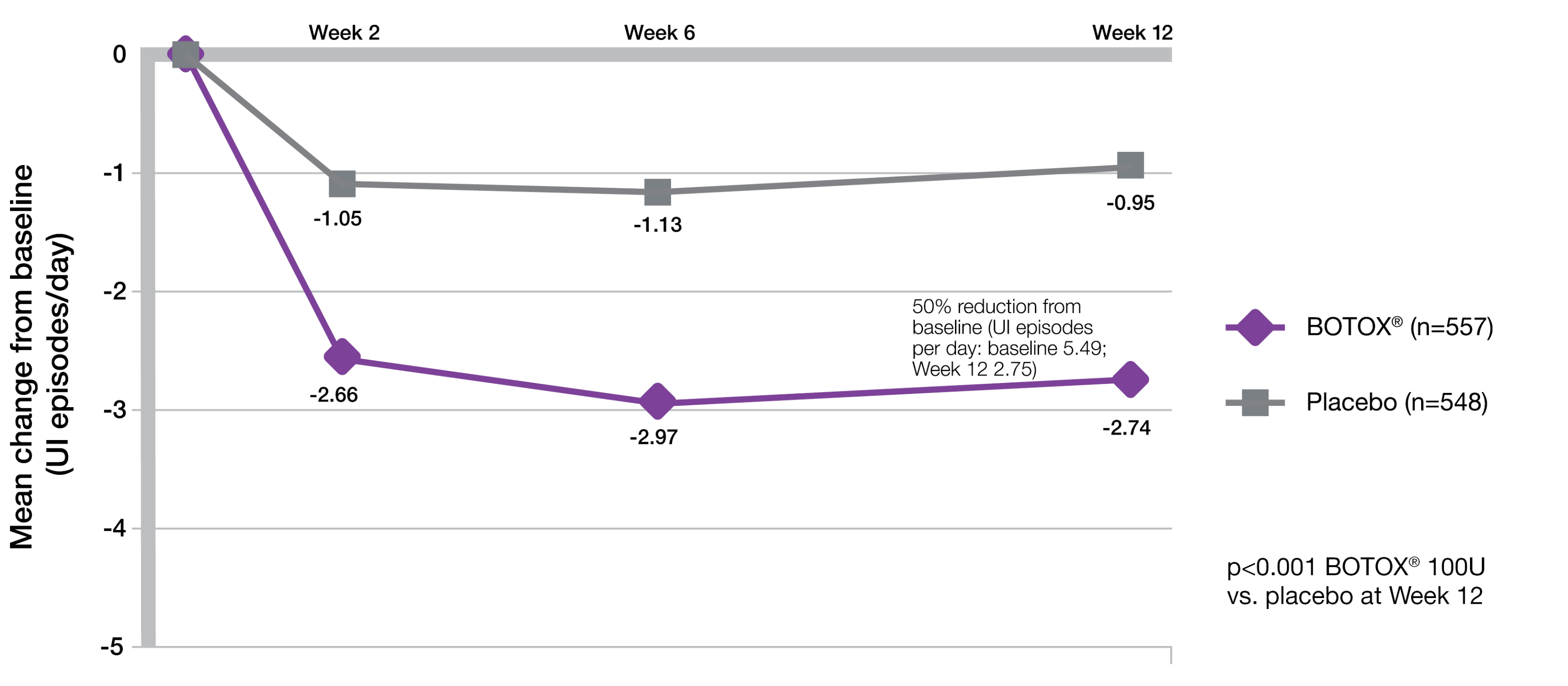
BOTOX® demonstrated significant reductions from baseline in daily UI episodes compared with placebo (-2.74 vs -0.95; p<0.001 vs placebo).5
Significantly greater proportion of BOTOX® patients achieved a positive response on the TBS compared to placebo (61.8% vs 28.0%; p<0.001 vs placebo).7
Study context: Two double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, 24-week phase 3 clinical studies were conducted in 1105 patients with overactive bladder, with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency and frequency, whose symptoms had not been adequately managed with at least one anticholinergic therapy. To evaluate the impact of efficacy, safety and health-related quality of life of BOTOX® in patients with OAB with UI. Patients were randomised to receive either 100U of BOTOX® (n=557) or placebo (n=548). Mean baseline for daily UI episodes: BOTOX® 100U 5.49/day, placebo 5.39/day. Mean baseline for daily urgency episodes: BOTOX® 100U 8.82/day, placebo 8.31/day.5
BOTOX® provides 50% reduction in UI episodes at week 12 vs baseline (co-primary endpoint)5-7
Adapted from BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics.5
Study context: Two double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, 24-week phase 3 clinical studies were conducted in 1105 patients with overactive bladder, with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency and frequency, whose symptoms had not been adequately managed with at least one anticholinergic therapy. Mean baseline daily UI episodes: BOTOX® 100U 5.49/day, placebo 5.39/day.5
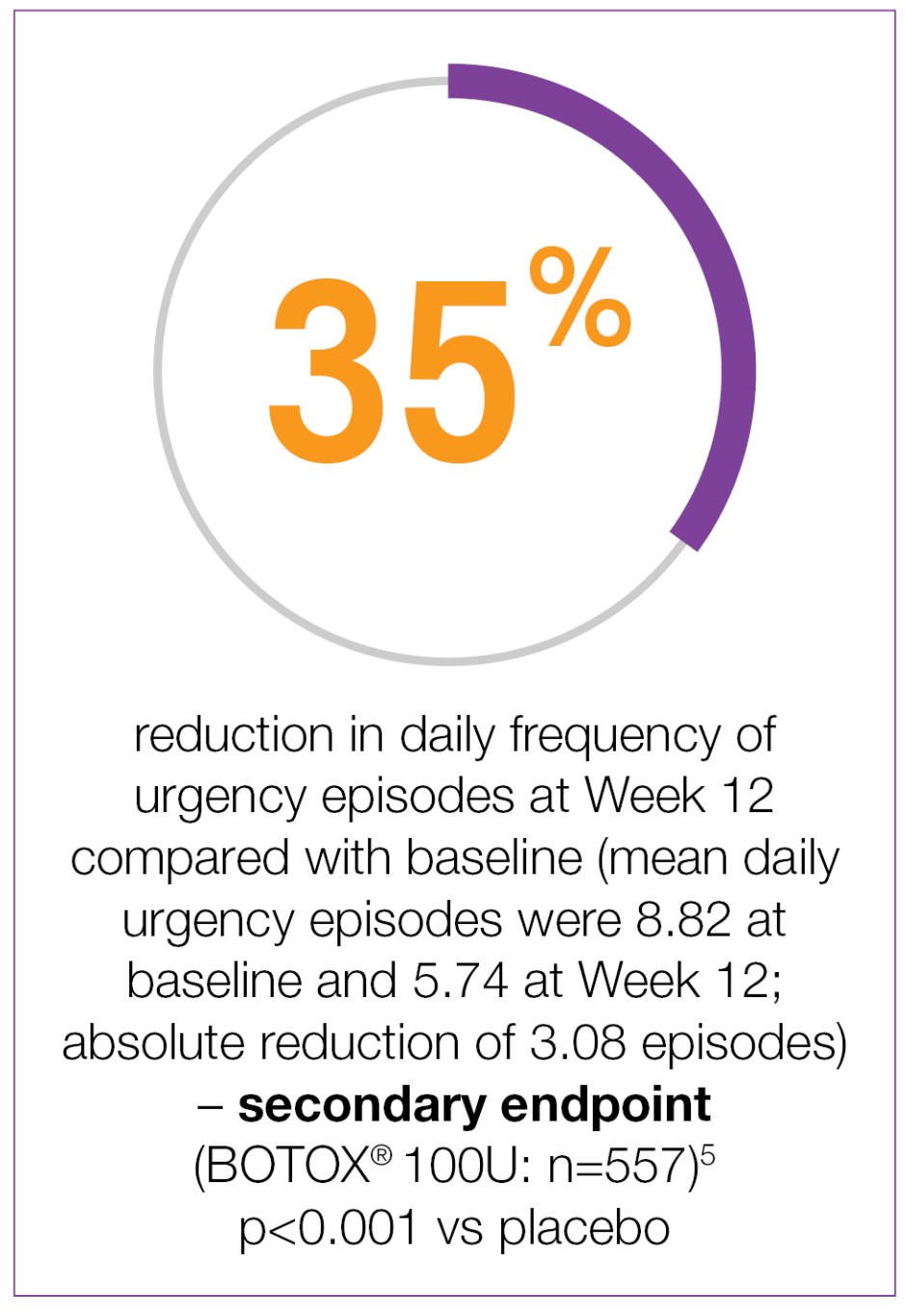
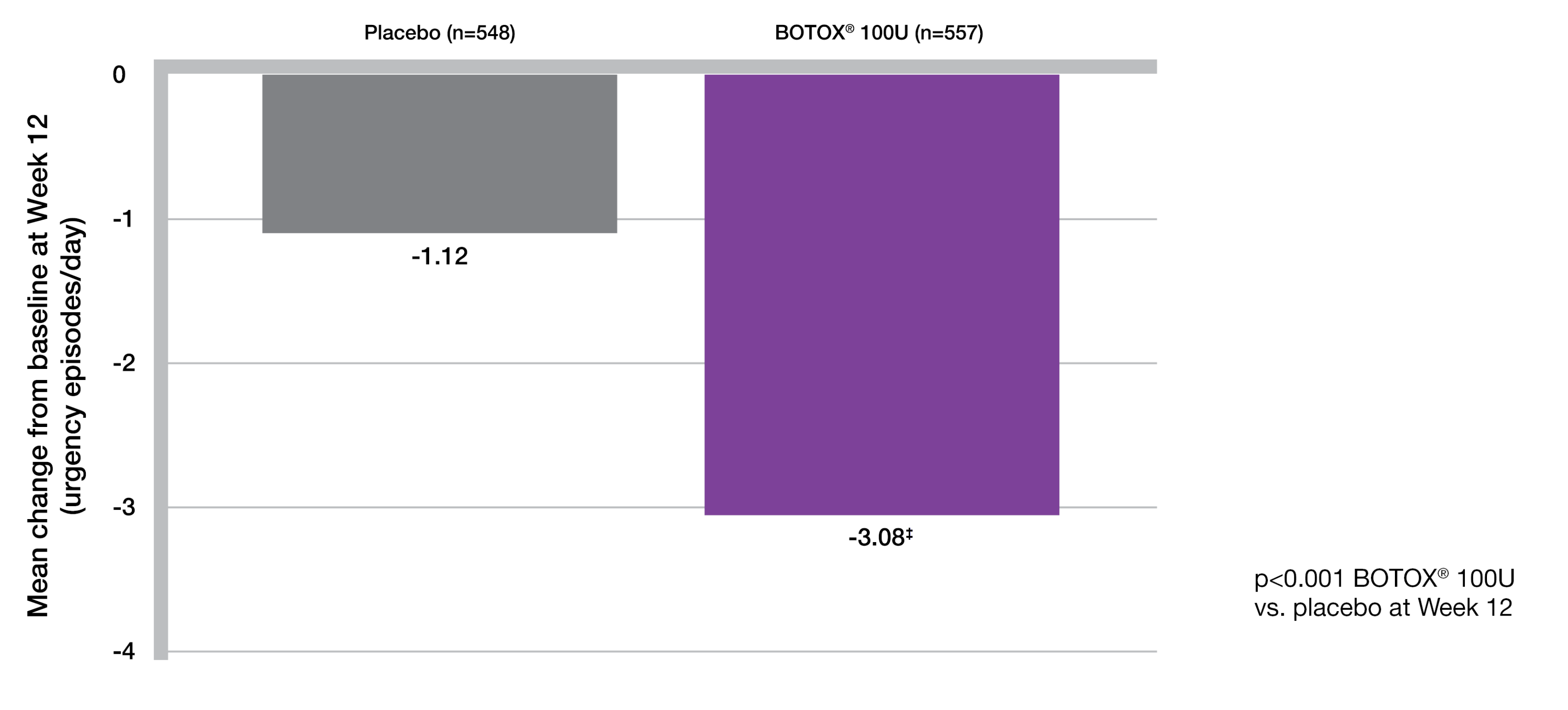
BOTOX® provides 35% reduction in urgency at week 12 vs baseline (secondary endpoint)5-7
Adapted from BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics.5
Study context: Two double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, 24-week phase 3 clinical studies were conducted in 1105 patients with overactive bladder, with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency and frequency, whose symptoms had not been adequately managed with at least one anticholinergic therapy. Patients were randomised to receive either 100U of BOTOX® (n=557) or placebo (n=548).5
‡Secondary endpoint. Mean baseline score: Placebo = 8.31/dey: BOTOX® 100U = 8.82/day. p<0.001 vs placebo. Co-primary end points were the change from baseline in the number of urinary incontinence episodes per day and the proportion of patients with a positive response on the treatment benefit scale at post-treatment week 12.5
Secondary end points were the change from baseline in daily frequency of micturition episodes, urgency episodes and health related quality of life.5
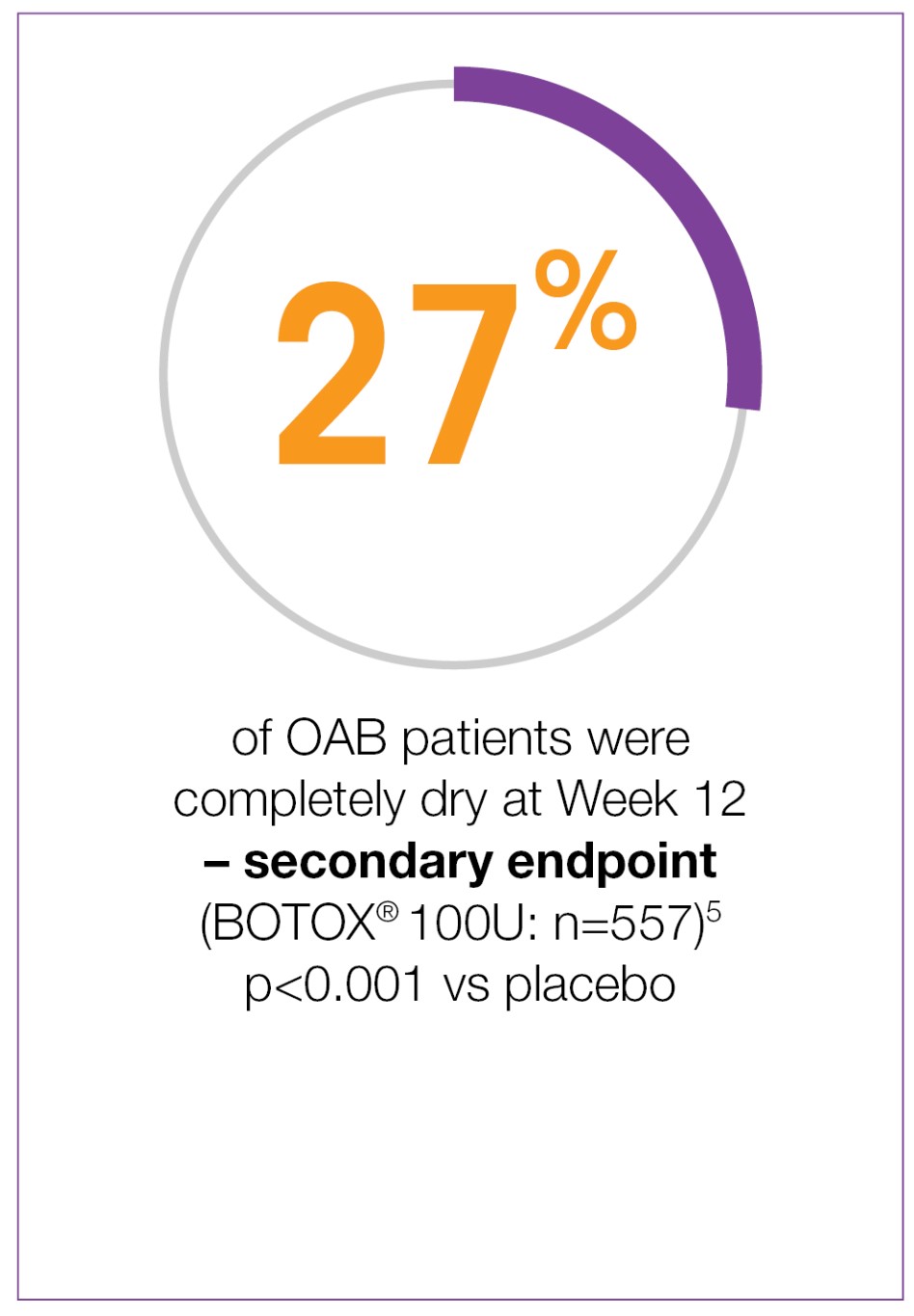
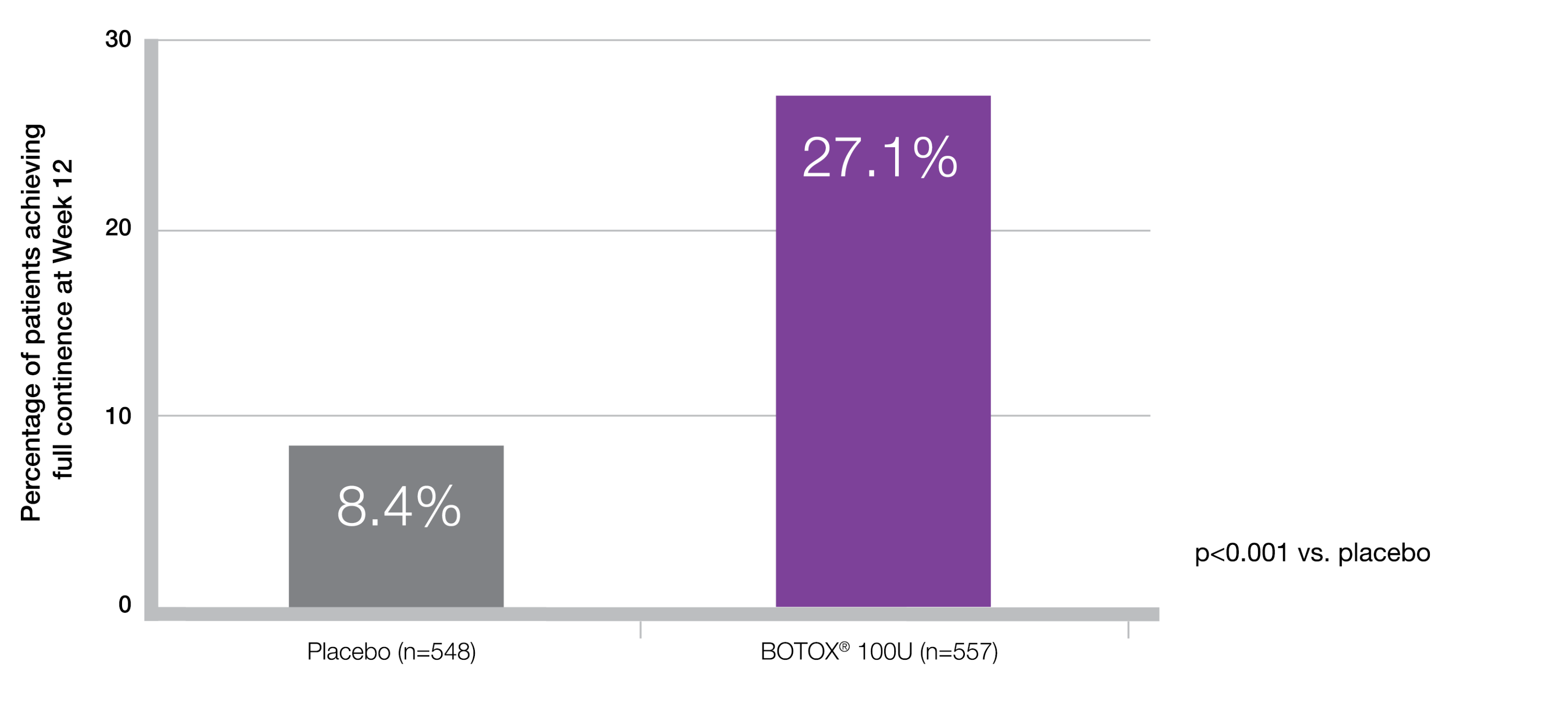
27% of patients were completely dry with BOTOX® at week 125-7‡
Adapted from BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics.5
Study context: Two double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, 24-week phase 3 clinical studies were conducted in 1105 patients with overactive bladder, with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency and frequency, whose symptoms had not been adequately managed with at least one anticholinergic therapy.5
‡Dry patients over a 3-day diary.
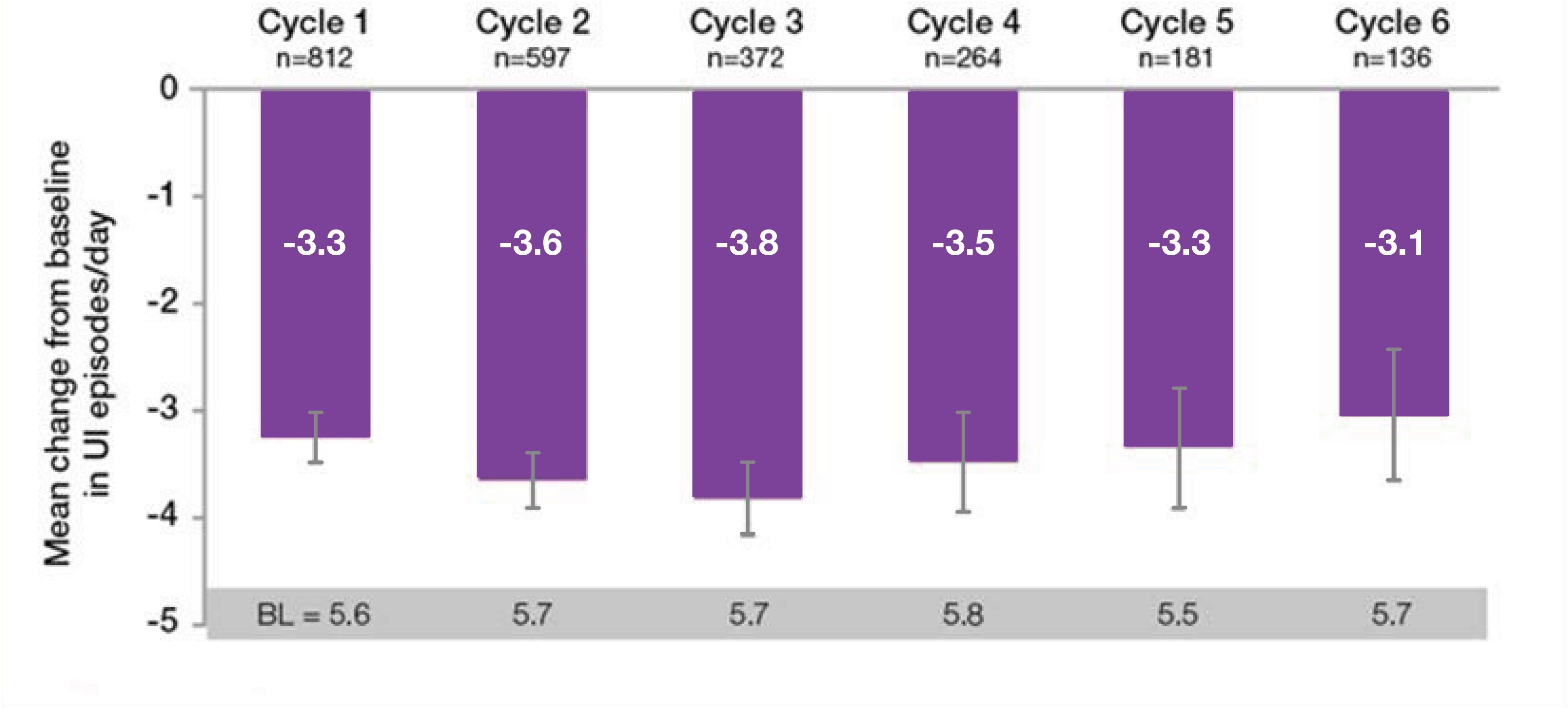
BOTOX® in OAB: Treatment benefit sustained over time6
BOTOX® sustained reductions in daily episodees of UI and urgency from baseline, throughout the entire 3.5 year study period6
Botulinum toxin type A 100U Treatment Number
Adapted from Nitti VW, et al. 20166
- Approximately 52% of patients completed the entire 3.5 year study6
- The most common reasons for discontinuation were related to study burden, personal reasons, loss to follow up and other non-treatment related reasons6
- Only 5.7% discontinued due to lack of efficacy and 5.1% due to adverse events efficacy and 5.1% due to adverse events6
Study context: The final results of the prospective, multicentre, long-term (3.5 year) study of the efficacy/safety of BOTOX® for overactive bladder syndrome. The co-primary endpoints were the mean reduction in UI episodes per day and the proportion of patients reporting a positive response on the treatment benefit scale. In the overall population the most common AEs within the first 12 weeks of BOTOX® treatment were localised to the urinary tract. There was no evidence of increasing occurence of these AEs with repeat treatments, UTI was the most frequently reported AE.6
†n values denote the number of patients with data avalable at Week 12. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
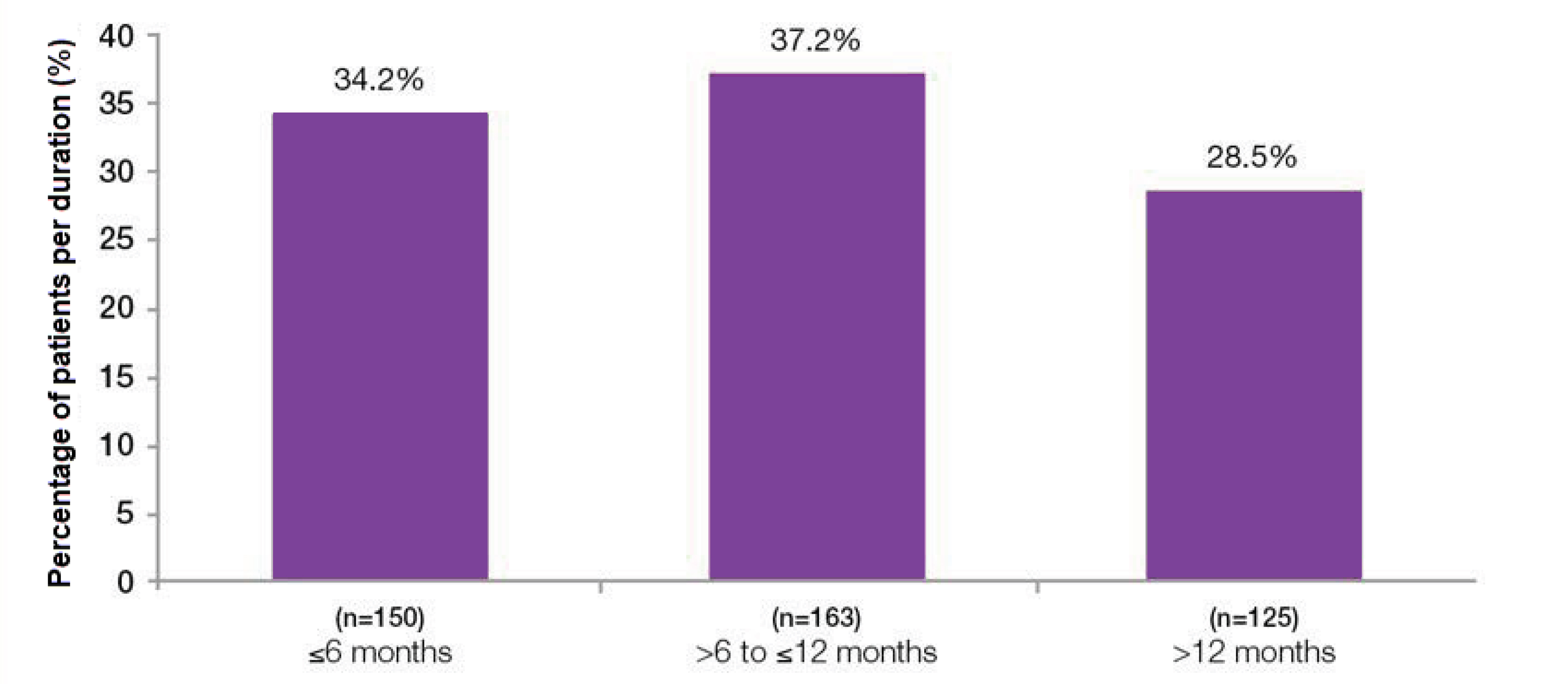
Overall median duration of effect was 7.6 months6
Duration of botulinum toxin type A effect based on time to patient request for re-treatment6
Adapted from Nitti VW, et al. 20166
Study context: The final results of the prospective, multicenter, long-term (3.5 year) study of the efficacy/safety of BOTOX® for overactive bladder syndrome. Median duration in patients (n=438) who received 100U BOTOX® only throughout study with complete treatment cycles, with 1 month defined as 4 weeks. Total study duration 3.5 years. Patients received up to 6 treatment cycles.6
AE: adverse event; BL: baseline; OAB: overactive bladder; TBS: treatment benefit scale; UI: urinary incontinence; UTI: urinary tract infection.
Please refer to the BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics for further information on adverse events, contraindications and special warnings and precautions for use. The BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics can be found here
By clicking the link above you will leave the AbbVie Pro website and be taken to the eMC PI portal website.
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at https://yellowcard.mhra.gov.uk/
Adverse events should also be reported to AbbVie on GBPV@abbvie.com
Date of preparation: June 2025. UK-BUO-250035.