The efficacy and safety of 24-hour continuous levodopa-based therapy with PRODUODOPA were demonstrated in 2 trials.1-3
IR=immediate-release.
Aim: Evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of PRODUODOPA to oral IR levodopa/carbidopa in patients with advanced PD.
Duration: 12 weeks.
Study type: Phase 3, 1:1 randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled.
Patient population: Evaluation of 141 patients. The target population was levodopa-responsive patients with advanced PD whose motor symptoms were inadequately controlled with current treatment and experienced minimum daily average of 2.5 hours of “Off” time per day, as assessed by PD diaries.*
Of the 74 patients randomized to receive PRODUODOPA, 48 completed the study and 26 discontinued treatment.
Of the 67 patients receiving optimized oral IR levodopa/carbidopa, 62 completed treatment and 5 discontinued.
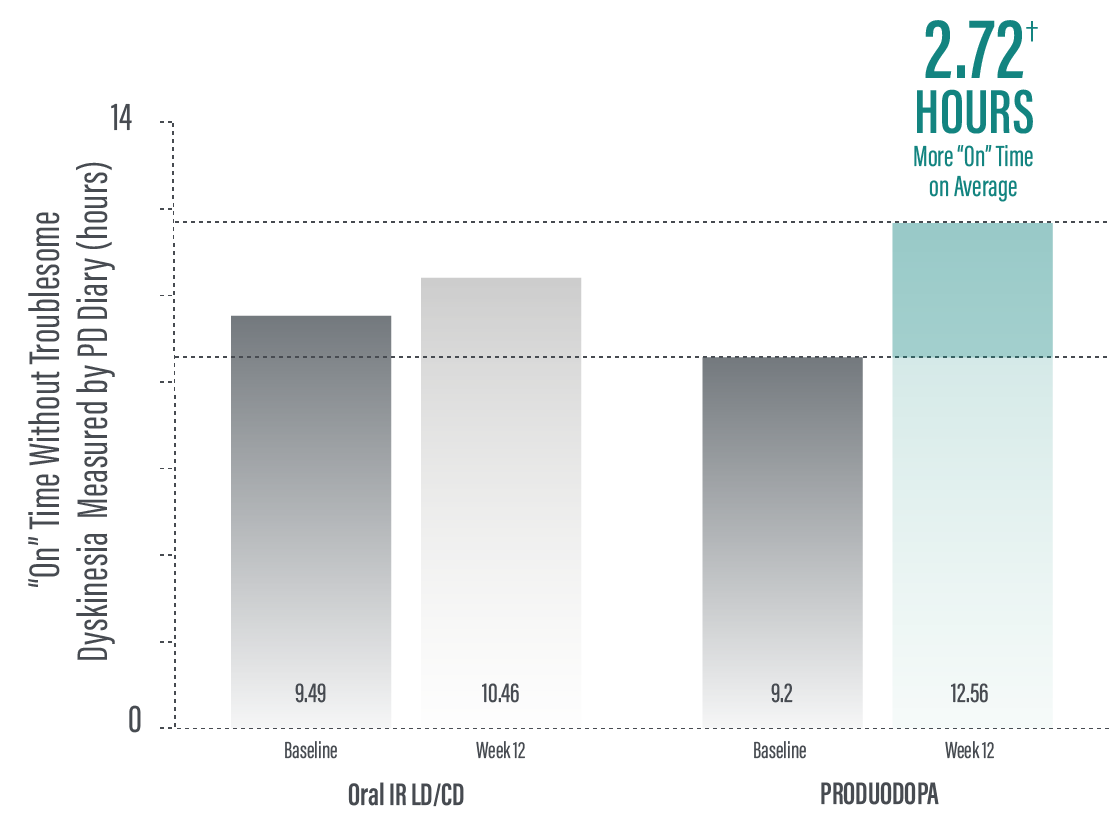
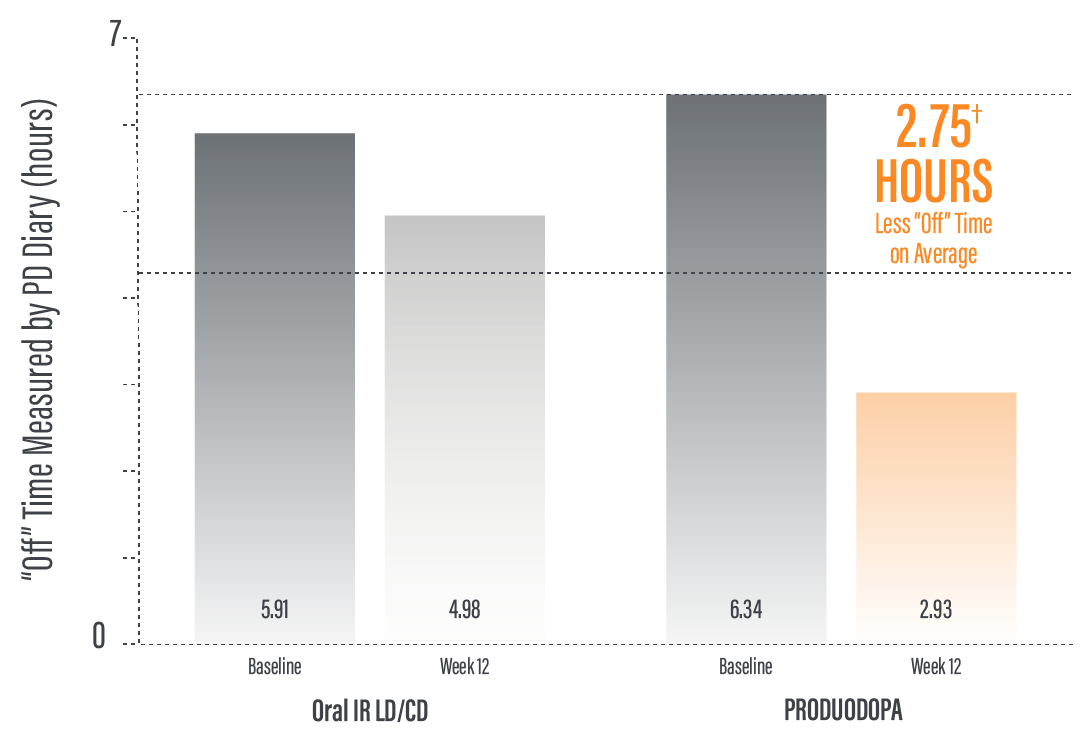
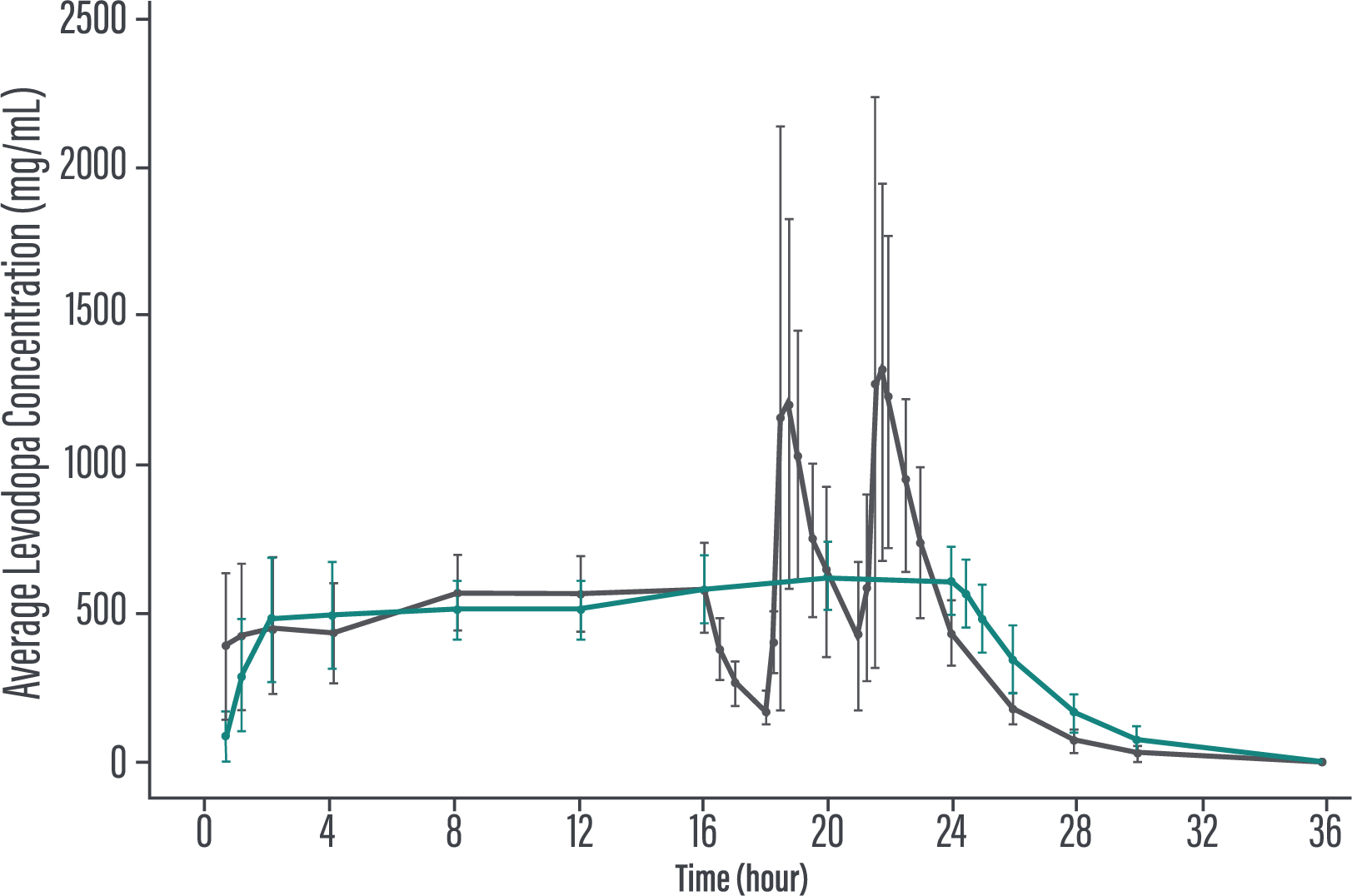
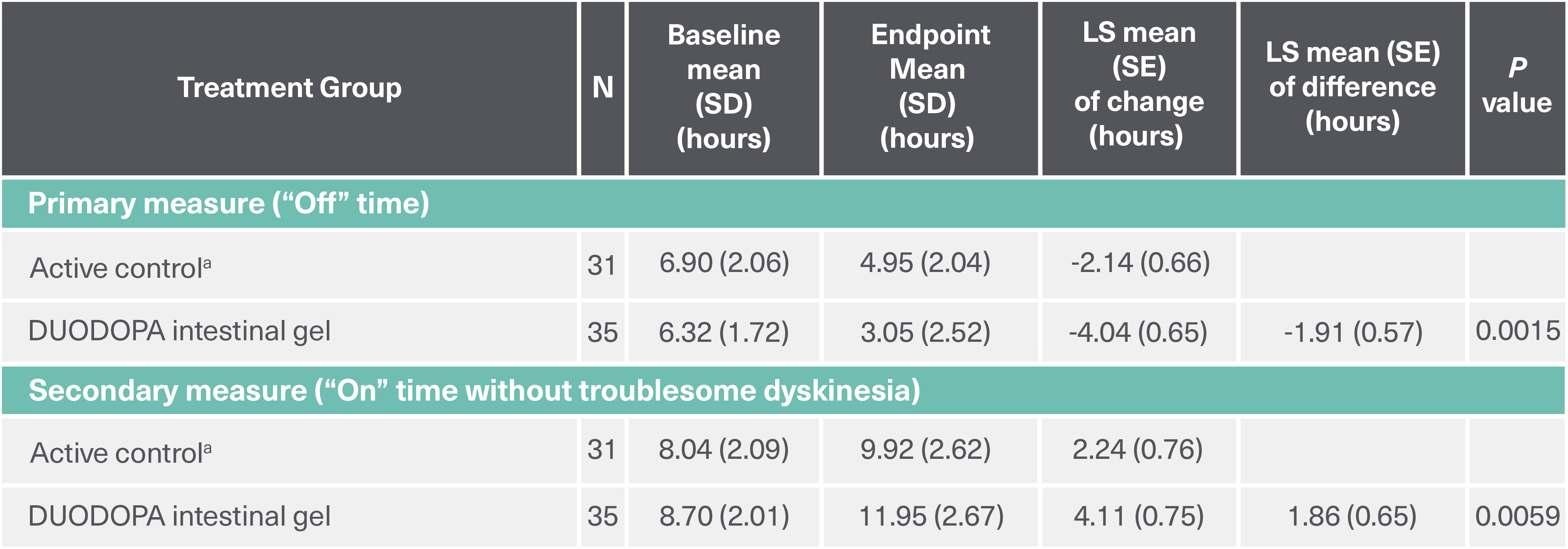
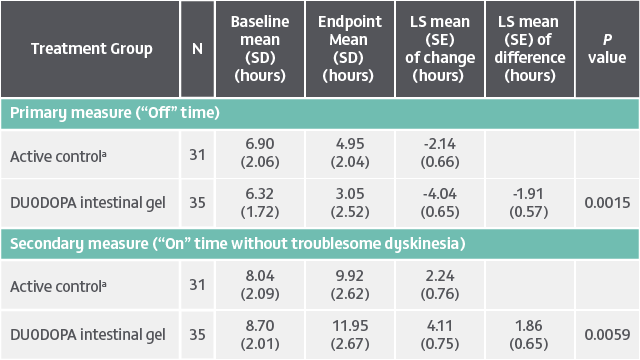
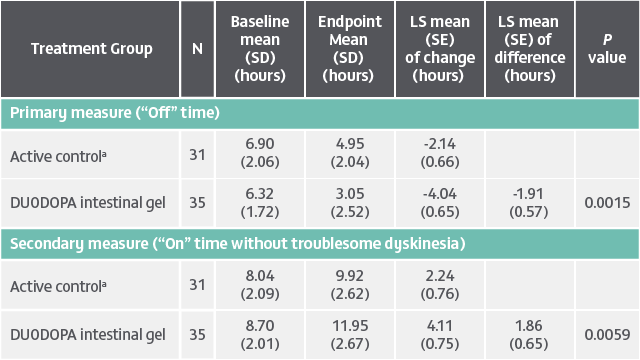
*Based on the PD diary, the average daily normalized “On” time for patients on PRODUODOPA was 9.20 (+/-2.42) hours at baseline and increased by 2.72 (+/-0.52) hours at Week 12 compared with an increase of 0.97 (+/-0.50) hours at Week 12 from a baseline of 9.49 (+/-2.62) hours for patients taking optimized IR levodopa/carbidopa (LS mean change [SE]). This resulted in a statistically significant improvement of 1.75 (+/-0.65) hours in patients on PRODUODOPA vs oral IR LD/CD (LS mean of difference [SE]; P=0.0083). Average daily normalized “Off” time for patients on PRODUODOPA was 6.34 (+/-2.27) hours at baseline and decreased by 2.75 (+/-0.50) hours at Week 12 compared with a decrease of 0.96 (+/-0.49) hours at Week 12 from a baseline of 5.91 (+/-1.88) hours for patients taking optimized IR levodopa/carbidopa (LS mean change [SE]). This resulted in a statistically significant improvement of 1.79 (+/-0.63) hours in patients on PRODUODOPA vs oral IR LD/CD (LS mean of difference [SE]; P=0.0054).1
IR=immediate-release; LD/CD=levodopa/carbidopa; PD=Parkinson’s disease; LS=least squares; SE=standard error.
*Patients recorded their PD symptoms in a PD Diary, which was completed for a full 24-hour period. Patients made an entry upon waking and every 30 minutes during their normal waking time and upon awakening from time asleep. Patients recorded their "On" time without troublesome dyskinesia (sum of "On" time without dyskinesia and "On" time without troublesome dyskinesia) and "Off" time as assessed by the PD Diary.3
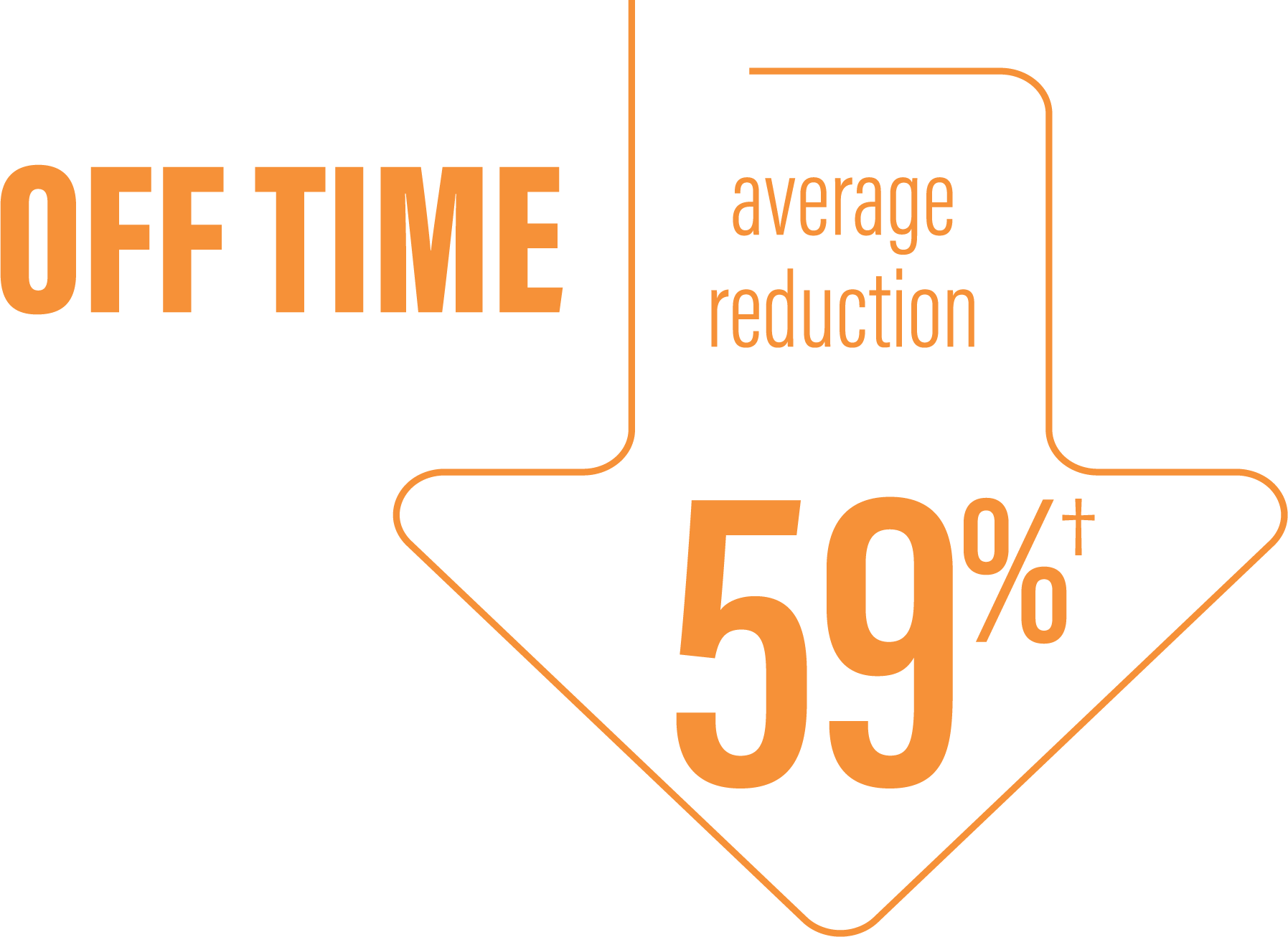
†More refers to improvement for patients on PRODUODOPA compared with oral IR levodopa/carbidopa in “On” and “Off” time at Week 12.3
IR=immediate-release; PD=Parkinson's disease.
(LS mean of difference=1.75 hours; P=0.0083)
*Based on the PD diary, the average daily normalized “On” time without troublesome dyskinesia for patients on PRODUODOPA was 9.20 (SD +/-2.42) hours at baseline and increased by 2.72 (SE +/-0.52) hours at Week 12 compared with an increase of 0.97 (SE +/-0.50) hours at Week 12 from a baseline of 9.49 (SD +/-2.62) hours for patients taking optimized IR levodopa/carbidopa (LS mean change [SE]). This resulted in a statistically significant improvement of 1.75 (SE +/-0.65) hours in patients on PRODUODOPA vs oral IR LD/CD (LS mean of difference [SE]; P=0.0083). “On” time without troublesome dyskinesia is the sum of “On” time without dyskinesia and “On” time with non‑troublesome dyskinesia.
†Model-based least square mean (standard error) of change.
‡Calculated by dividing the change in hours from baseline by the number of hours reported at baseline.
IR=immediate-release; LS=least squares; PD=Parkinson's disease; SD=standard deviation; SE=standard error; LD/CD=levodopa/carbidopa.
(LS mean of difference=-1.79 hours; P=0.0054)
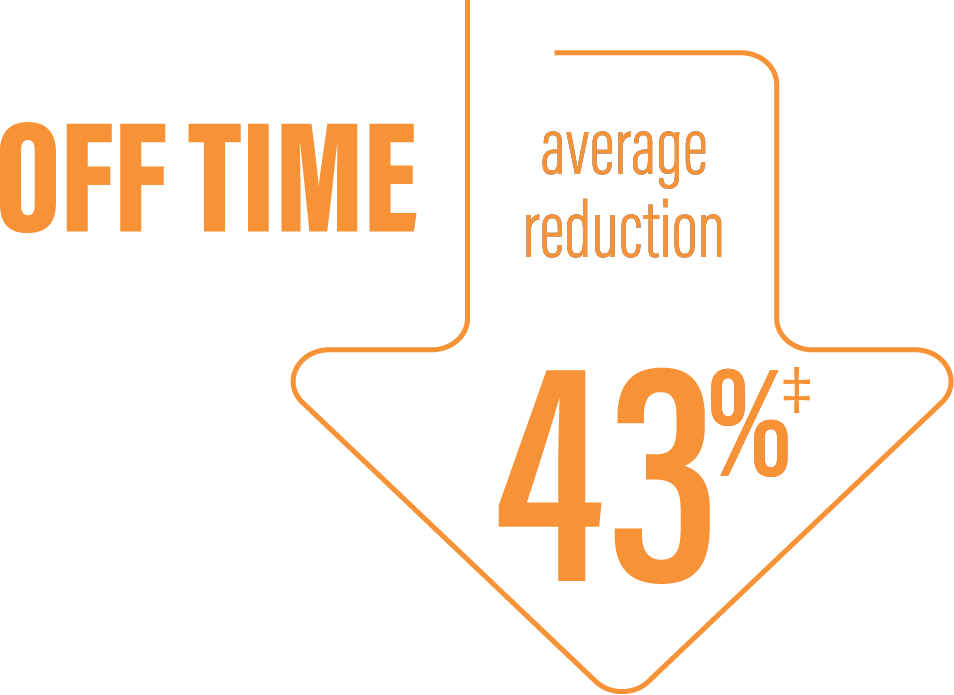
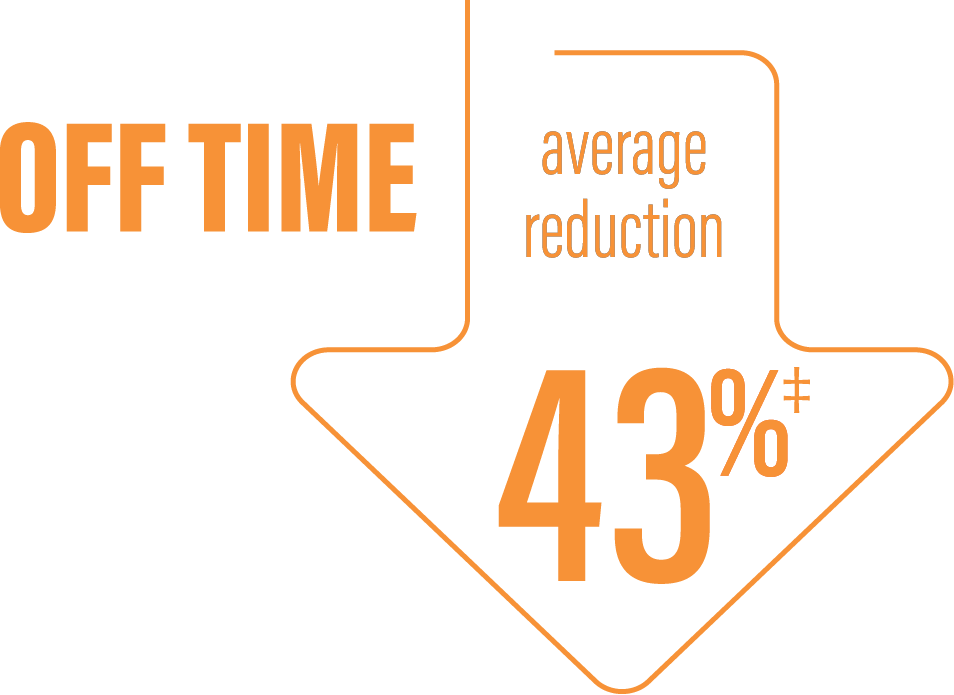
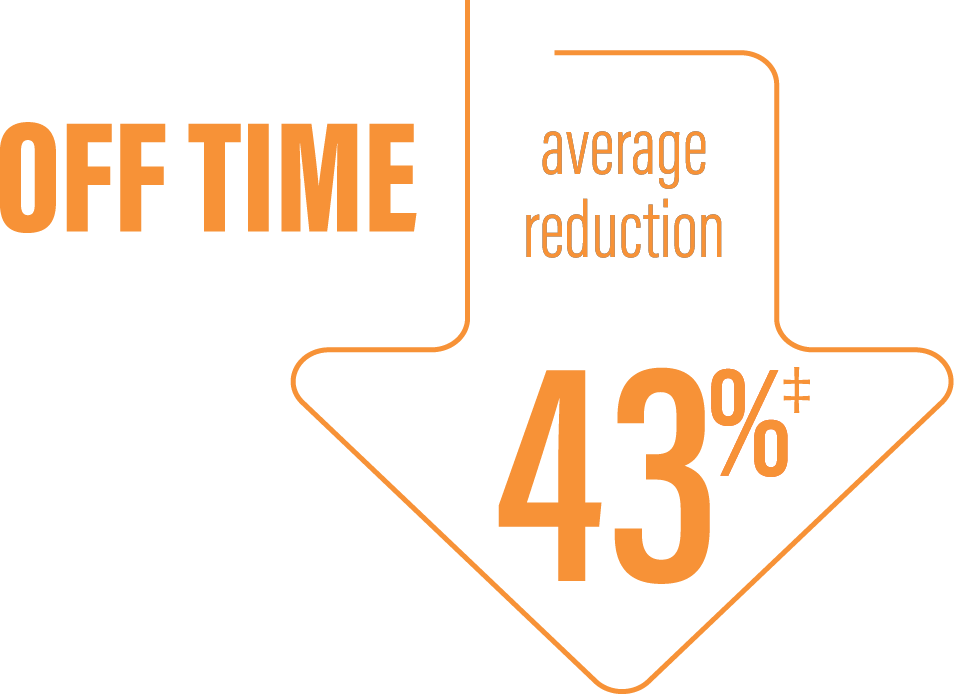
*Based on the PD diary, the average daily normalized “Off” time for patients on PRODUODOPA was 6.34 (SD +/-2.27) hours at baseline and decreased by 2.75 (SE +/-0.50) hours at Week 12 compared with a decrease of 0.96 (SE +/-0.49) hours at Week 12 from a baseline of 5.91 (SD +/-1.88) hours for patients taking optimized IR levodopa/carbidopa (LS mean change [SE]). This resulted in a statistically significant improvement of 1.79 (SE +/-0.63) hours in patients on PRODUODOPA vs oral IR LD/CD (LS mean of difference [SE]; P=0.0054).
†Model-based least square mean (standard error) of change.
‡Calculated by dividing the change in hours from baseline by the number of hours reported at baseline.
IR=immediate-release; LD/CD=levodopa/carbidopa; LS=least squares; PD=Parkinson's disease; SD=standard deviation; SE=standard error.
Note to affiliate: Morning akinesia has been included within the Study 736 publication and is being reviewed as part of the "Type II variation SmPC assessment" by MPA. Please assess inclusion of morning akinesia information data based on your local rules and regulations
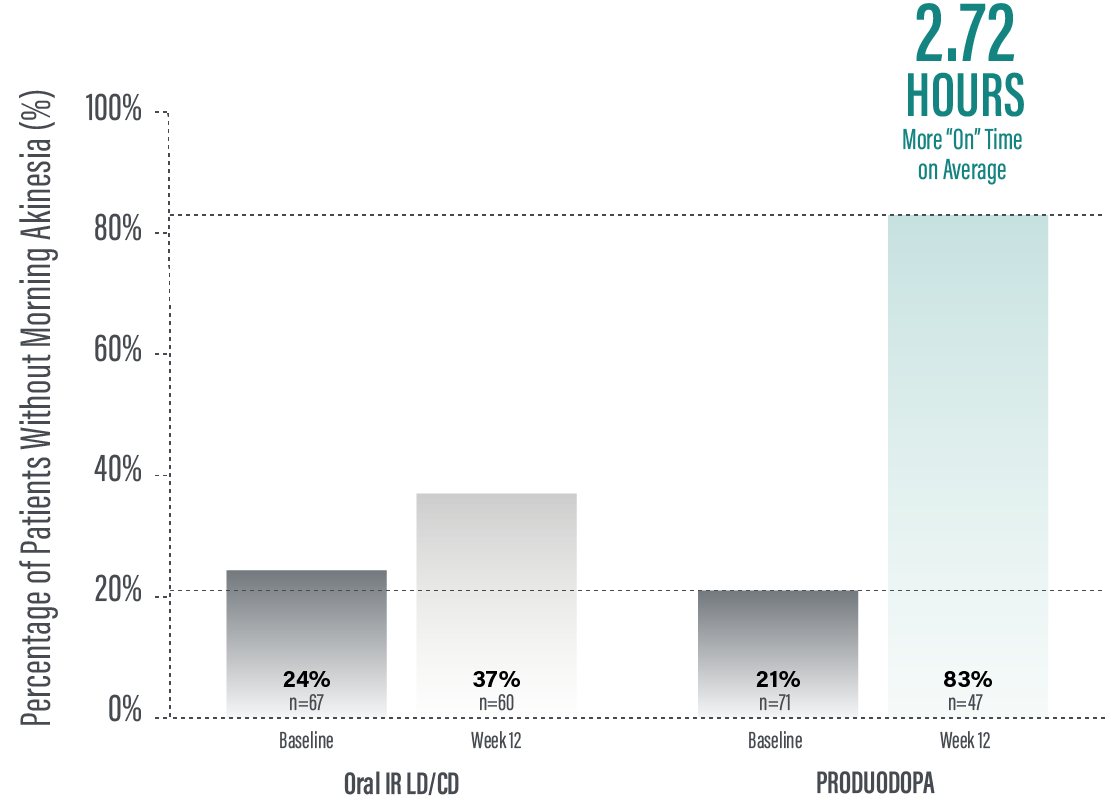
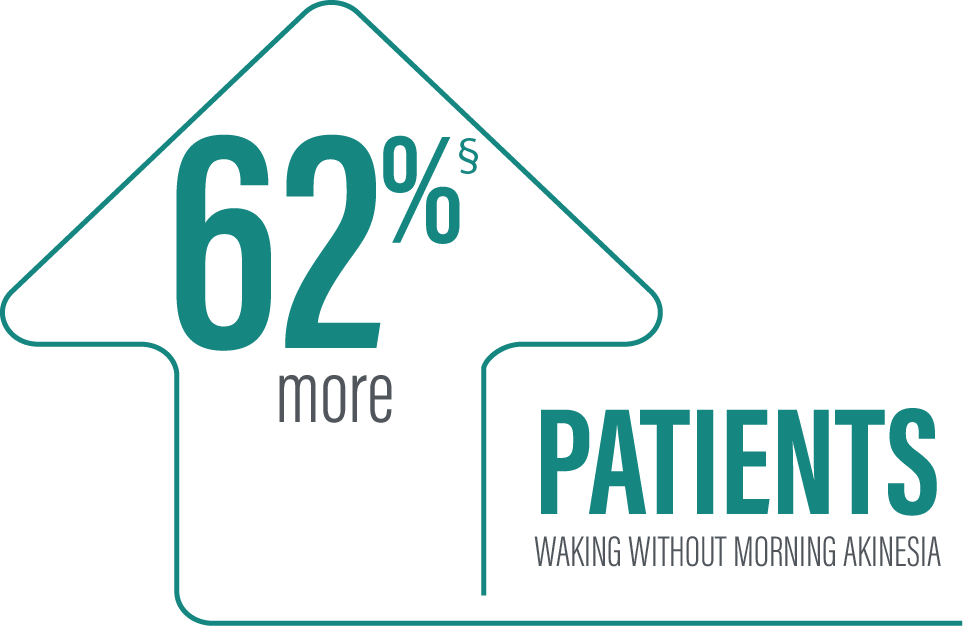
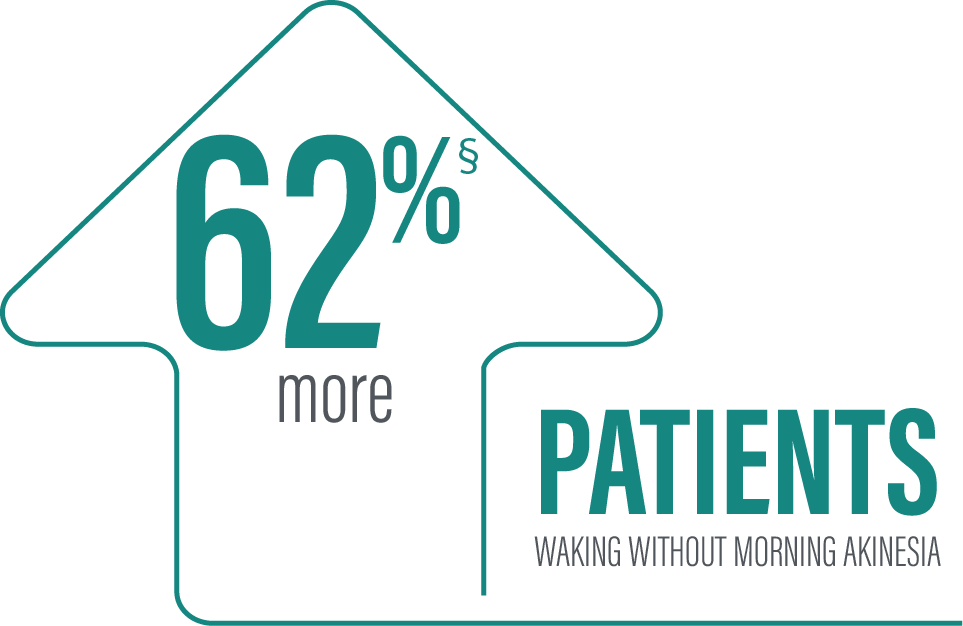
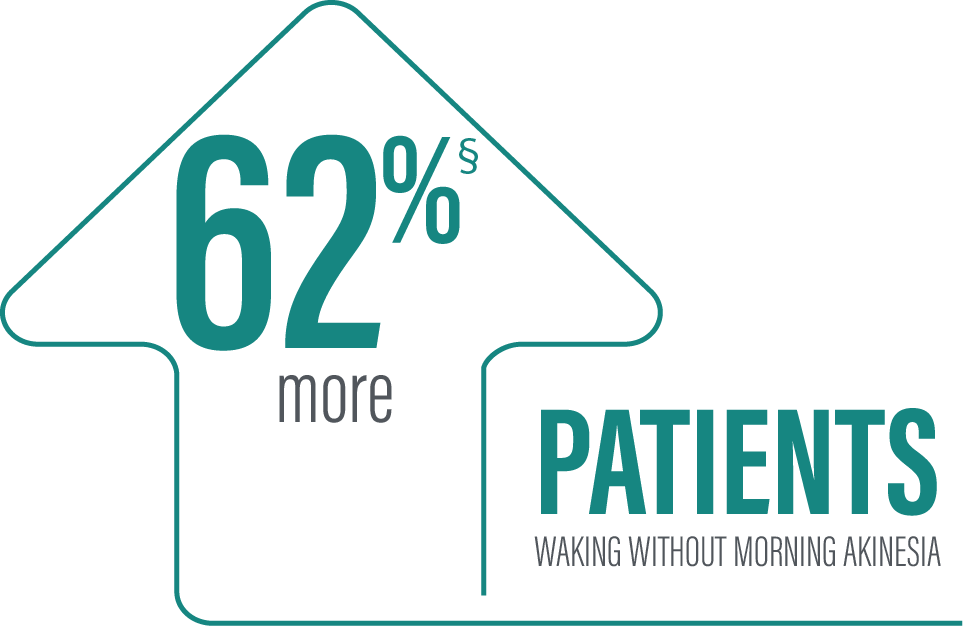
Secondary efficacy endpoints were tested in hierarchical order. Hierarchical testing ended after the first secondary endpoint as the next prespecified endpoint did not reach significance.3 PRODUODOPA demonstrated improvements at Week 12 in morning akinesia compared to baseline, but did not achieve statistical significance when compared to active control arm.1
*Morning akinesia was defined as reporting “Off” status as the first morning symptom upon awakening.
†Percentage of patients without morning akinesia is the sum of patients reporting “On” time without dyskinesia, “On” time with non-troublesome dyskinesia, and “On” time with troublesome dyskinesia upon awakening.
‡Based on the PD diary, patients on PRODUODOPA, “On” without dyskinesia was reported in 70% (33/47) of patients; “On” with nontroublesome dyskinesia was reported in 8% (4/47) of patients; “On” with troublesome dyskinesia was reported in 4% (2/47) of patients. For patients on oral IR LD/CD “On” without dyskinesia was reported in 37% (22/60) of patients. Based on the PD diary, 79% (56/71) of patients on PRODUODOPA experienced morning akinesia at baseline and decreased to 17% (8/47) of patients at Week 12. By comparison, 76% (51/67) of patients taking optimized oral IR LD/CD experienced morning akinesia at baseline and decreased to 63% (38/60) of patients at Week 12.
§Calculated by dividing the change in hours from baseline by the number of hours reported at baseline.
IR=immediate-release; LD/CD=levodopa/carbidopa; PD=Parkinson’s disease.
Aim: Evaluate the safety and tolerability of 24-hour daily exposure with a continuous subcutaneous infusion of PRODUODOPA. Secondary efficacy endpoints were also evaluated.
Duration: 52 weeks (this study is ongoing).
Study type: Phase 3, single-arm, open-label.
Patient population: Evaluation of 244 patients. 137 patients completed the 52-week study. The target population was levodopa-responsive patients with PD whose motor symptoms were inadequately controlled with current treatment and experienced a minimum of 2.5 hours of “Off” time per day as assessed by PD diaries.*
PD=Parkinson’s disease.
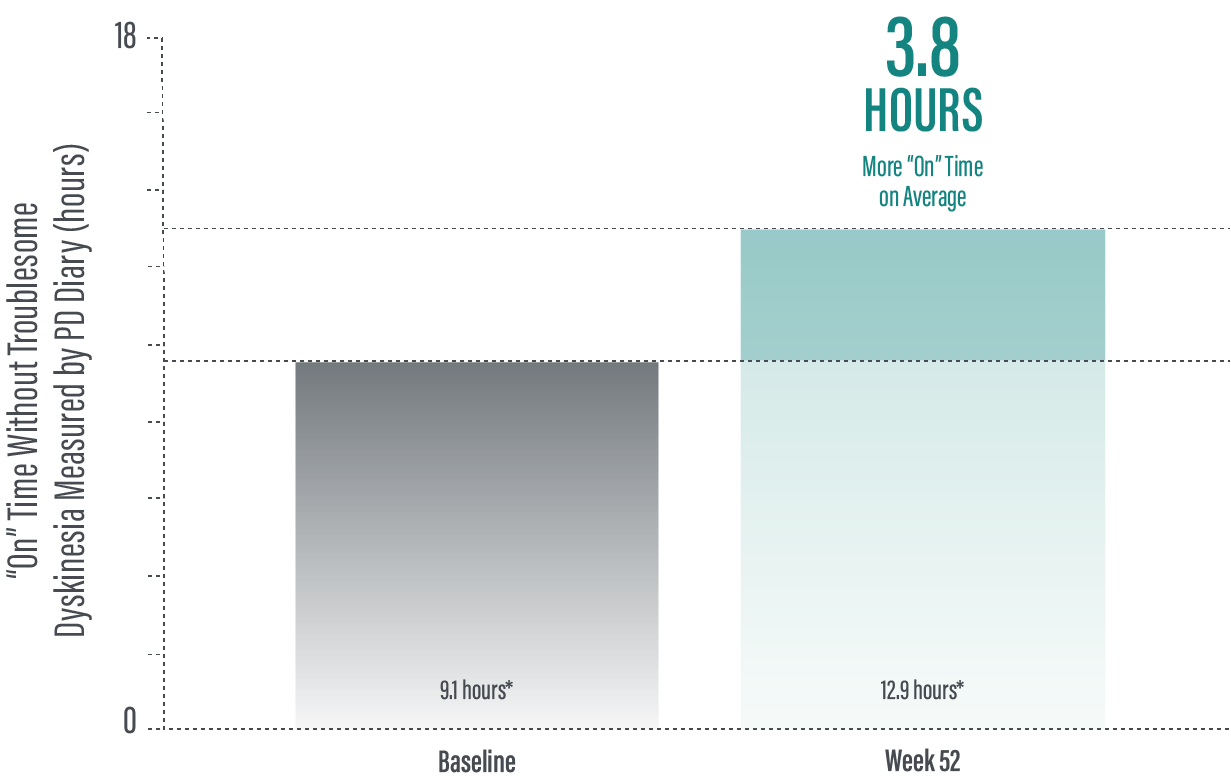
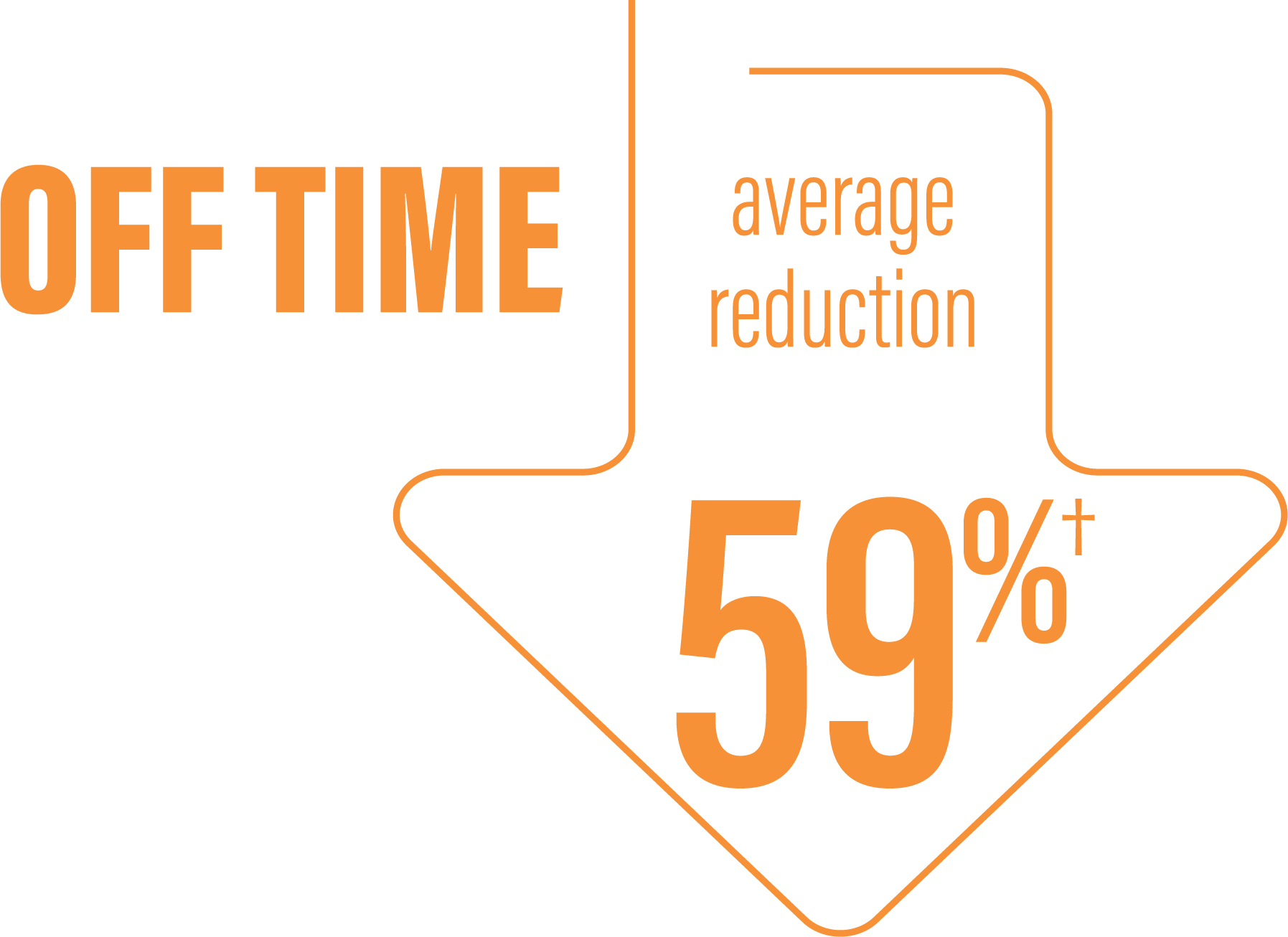
The PRODUODOPA safety study is ongoing. Data presented reflect the third interim analysis of 52-week study results that include 104 patients. “On” time without troublesome dyskinesia improved by an average of 3.8 (+/-3.3) hours by Week 52 (average 12.9 hours*) compared to baseline (average 9.1 [+/-2.5] hours*; n=236)
(P≤0.001) based on the PD diary.1,2
*Values represent unadjusted mean hours (+/-standard deviation) assessed using a 24-hour PD diary and normalised to a 16-hour waking day. Only patients who completed each study visit were included in the efficacy analysis, and no adjustments were made to account for premature discontinuation.
†Calculated by dividing the change in hours from baseline by the number of hours reported at baseline.
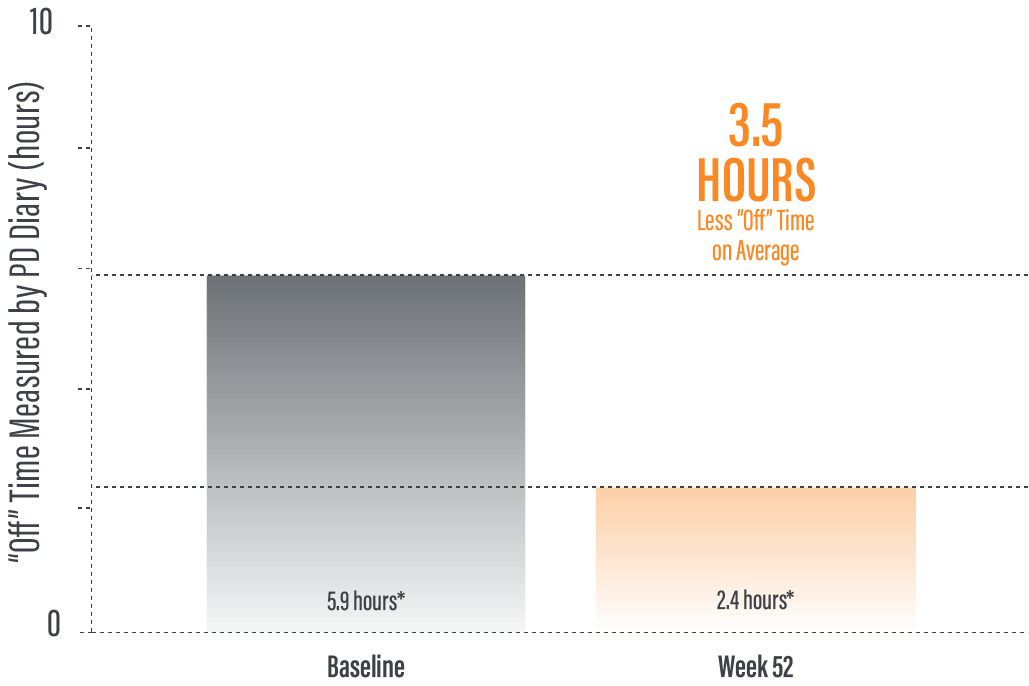
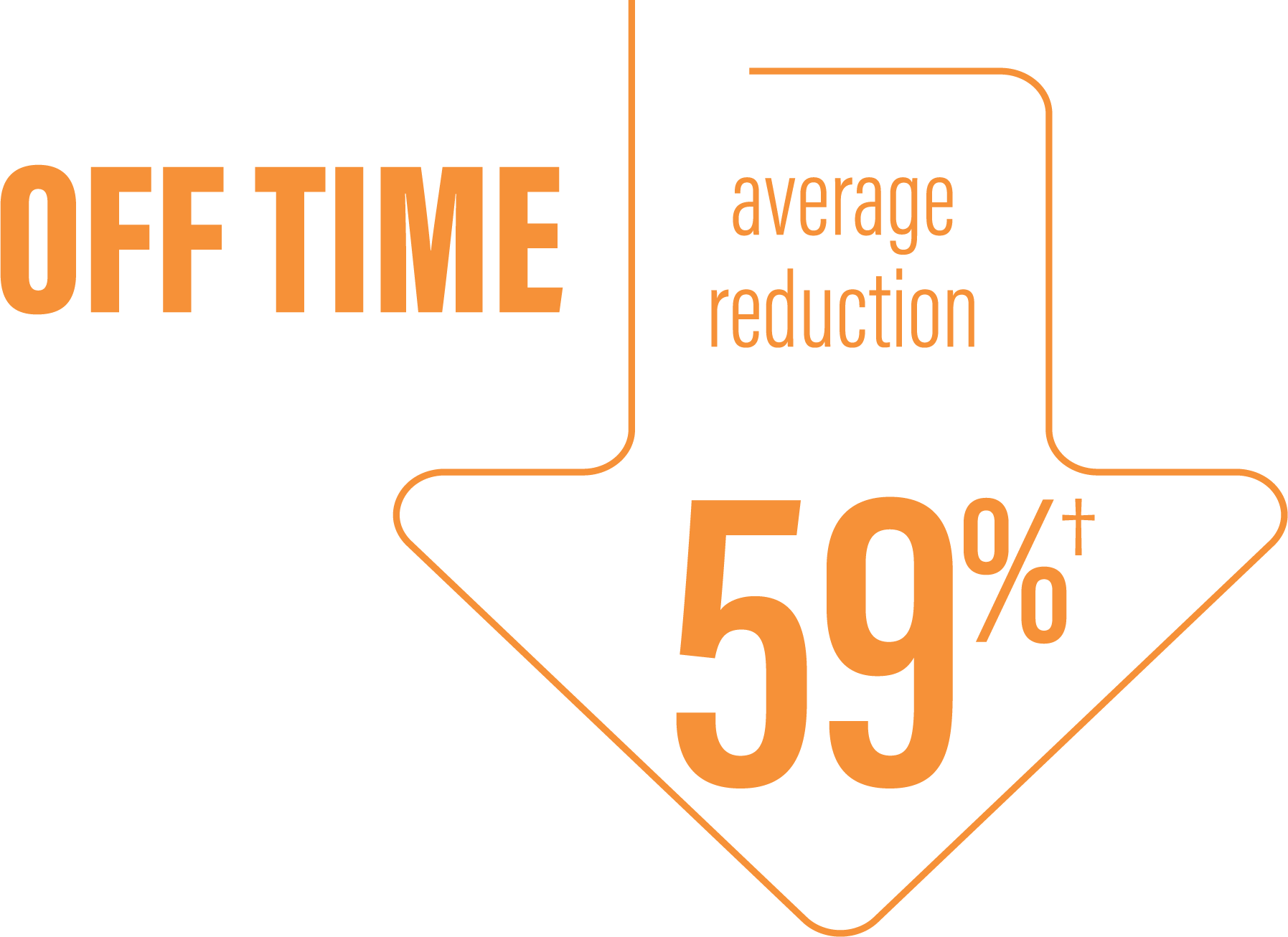
The PRODUODOPA safety study is ongoing. Data presented reflect the third interim analysis of 52-week study results that include 104 patients. “Off” time was decreased by an average of 3.5 (+/-3.1) hours by Week 52 (average 2.4 hours) compared to baseline (average 5.9 [+/-2.2] hours*; n=236) (P≤0.001) based on the PD diary.1,2
*Values represent unadjusted mean hours (+/-standard deviation) assessed using a 24-hour PD diary and normalised to a 16-hour waking day. Only patients who completed each study visit were included in the efficacy analysis, and no adjustments were made to account for premature discontinuation.
†Calculated by dividing the change in hours from baseline by the number of hours reported at baseline.
Continue to Safety page
Please refer to the PRODUODOPA SmPC for complete Prescribing and Safety Infomation.