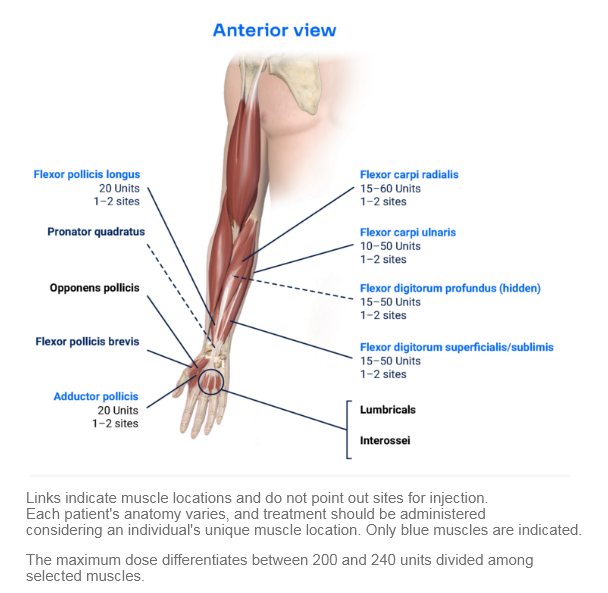
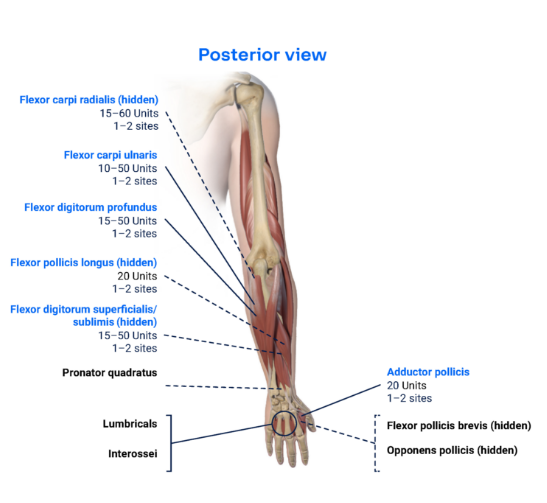
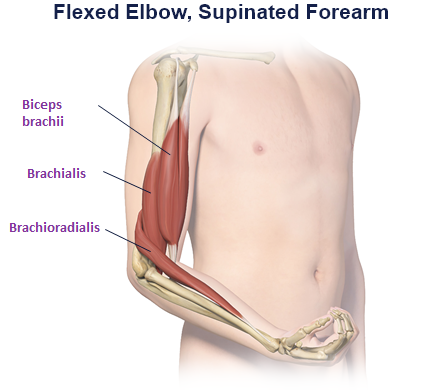
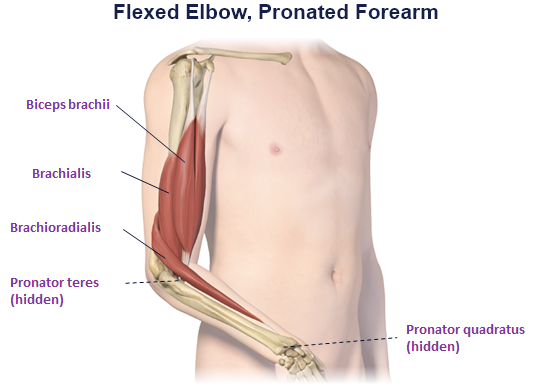
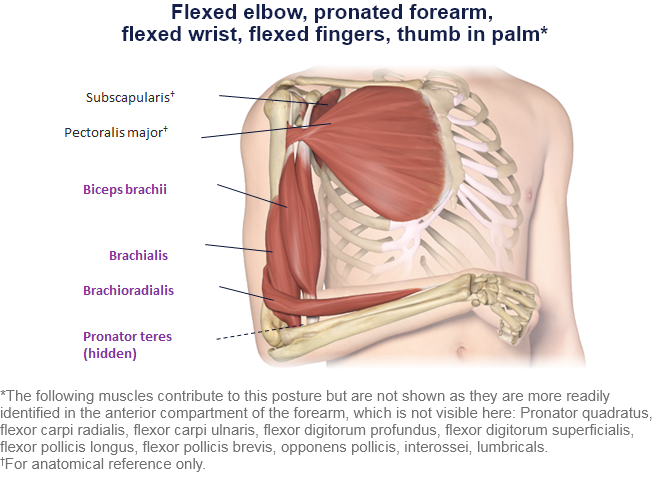
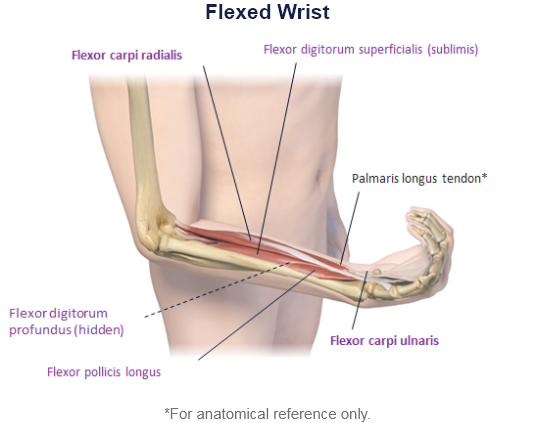
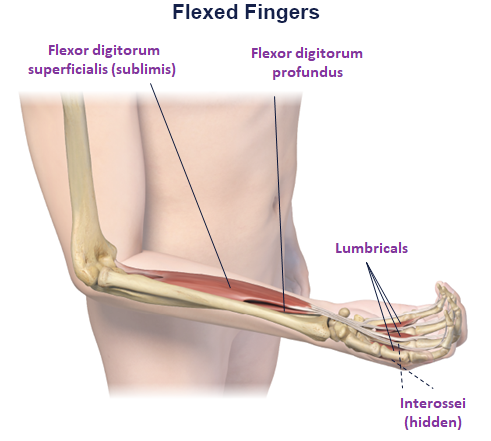
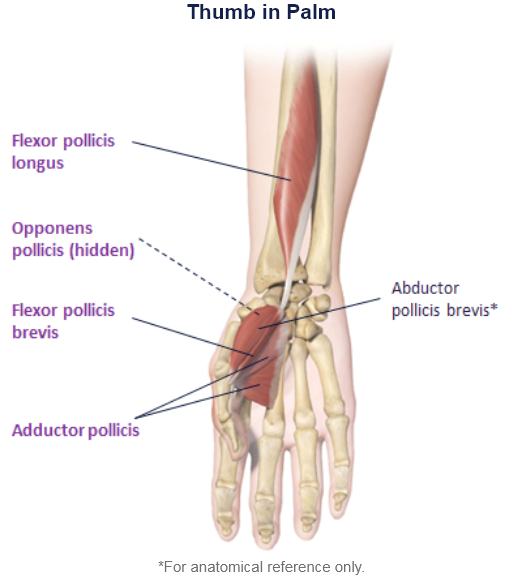
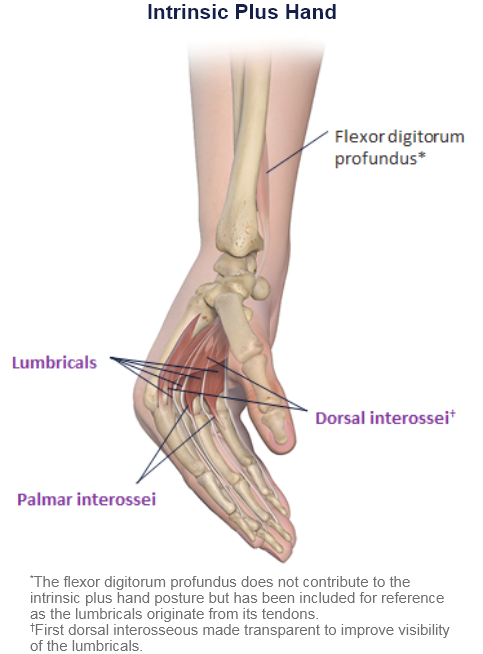
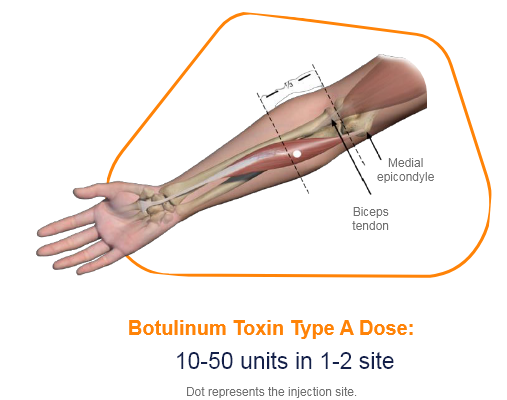
Clinical Presentation Pattern and Associated Muscles
Injection Sites
Patterns and Clinical Presentations
The flexor carpi radialis muscle is lateral to the palmaris longus and has a large and prominent tendon in the distal half of the forearm.
Unlike the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris, which forms the medial margin of the distal forearm, the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle is positioned just lateral to the midline. In this position, the tendon can be easily palpated, making it an important landmark for finding the pulse in the radial artery, which lies immediately lateral to it.1
• Function: Flexion and adduction at the wrist.2
• Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus.2
• Insertion: Base of second metacarpal.2
• Innervation: Median nerve (C6, C7).2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
The flexor carpi radialis muscle is lateral to the palmaris longus and has a large and prominent tendon in the distal half of the forearm.
Unlike the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris, which forms the medial margin of the distal forearm, the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle is positioned just lateral to the midline. In this position, the tendon can be easily palpated, making it an important landmark for finding the pulse in the radial artery, which lies immediately lateral to it.1
• Function: Flexion and adduction at the wrist.2
• Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus.2
• Insertion: Base of second metacarpal.2
• Innervation: Median nerve (C6, C7).2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
The flexor carpi radialis muscle is lateral to the palmaris longus and has a large and prominent tendon in the distal half of the forearm.
Unlike the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris, which forms the medial margin of the distal forearm, the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle is positioned just lateral to the midline. In this position, the tendon can be easily palpated, making it an important landmark for finding the pulse in the radial artery, which lies immediately lateral to it.1
• Function: Flexion and adduction at the wrist.2
• Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus.2
• Insertion: Base of second metacarpal.2
• Innervation: Median nerve (C6, C7).2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
The flexor carpi radialis muscle is lateral to the palmaris longus and has a large and prominent tendon in the distal half of the forearm.
Unlike the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris, which forms the medial margin of the distal forearm, the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle is positioned just lateral to the midline. In this position, the tendon can be easily palpated, making it an important landmark for finding the pulse in the radial artery, which lies immediately lateral to it.1
• Function: Flexion and adduction at the wrist.2
• Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus.2
• Insertion: Base of second metacarpal.2
• Innervation: Median nerve (C6, C7).2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
The flexor carpi radialis muscle is lateral to the palmaris longus and has a large and prominent tendon in the distal half of the forearm.
Unlike the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris, which forms the medial margin of the distal forearm, the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle is positioned just lateral to the midline. In this position, the tendon can be easily palpated, making it an important landmark for finding the pulse in the radial artery, which lies immediately lateral to it.1
• Function: Flexion and adduction at the wrist.2
• Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus.2
• Insertion: Base of second metacarpal.2
• Innervation: Median nerve (C6, C7).2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
The flexor carpi radialis muscle is lateral to the palmaris longus and has a large and prominent tendon in the distal half of the forearm.
Unlike the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris, which forms the medial margin of the distal forearm, the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle is positioned just lateral to the midline. In this position, the tendon can be easily palpated, making it an important landmark for finding the pulse in the radial artery, which lies immediately lateral to it.1
• Function: Flexion and adduction at the wrist.2
• Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus.2
• Insertion: Base of second metacarpal.2
• Innervation: Median nerve (C6, C7).2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
References
1. Mitchell, Adam & drake, & Vogl, A.. (2015). Gray's Anatomy for Students, 3rd Edition.
2. Javed, O., Maldonado, K.A. and Ashmyan, R. (2022). Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Muscles. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
3. Lung, B.E. and Siwiec, R.M. (2018). Anatomy, Shoulder and upper limb, forearm flexor carpi ulnaris muscle.
4. Okafor, L. and Varacallo, M. (2019). Anatomy, shoulder and upper limb, hand flexor digitorum superficialis muscle.
5. Lung, B.E. and Burns, B. (2018). Anatomy, shoulder and upper limb, hand flexor digitorum profundus muscle.
6. Benson, D.C., Miao, K.H. and Varacallo, M.(2021). Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Flexor Pollicis Longus Muscle. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
7. Acosta, J.R., Graefe, S.B. and Varacallo, M., 2018. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Adductor Pollicis.