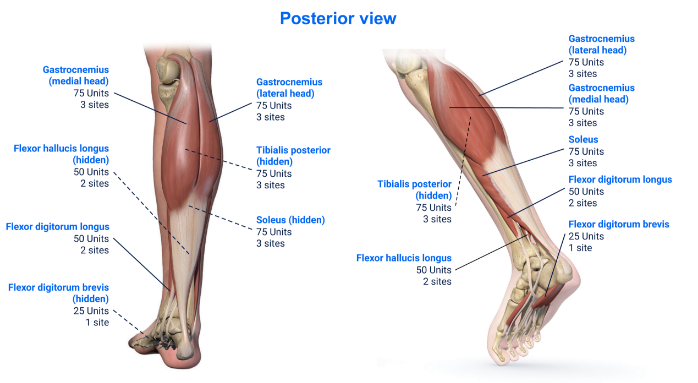
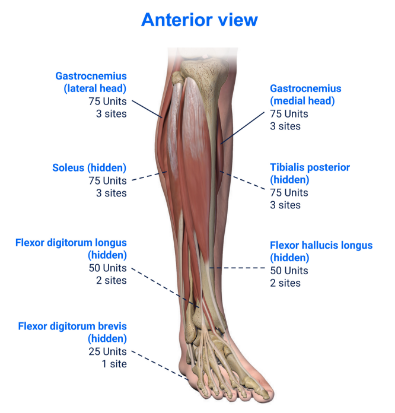
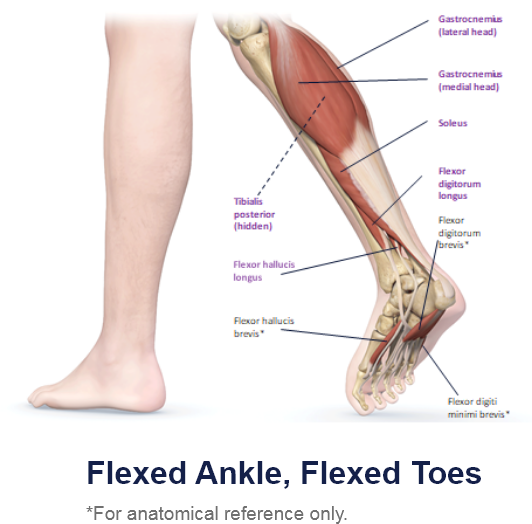
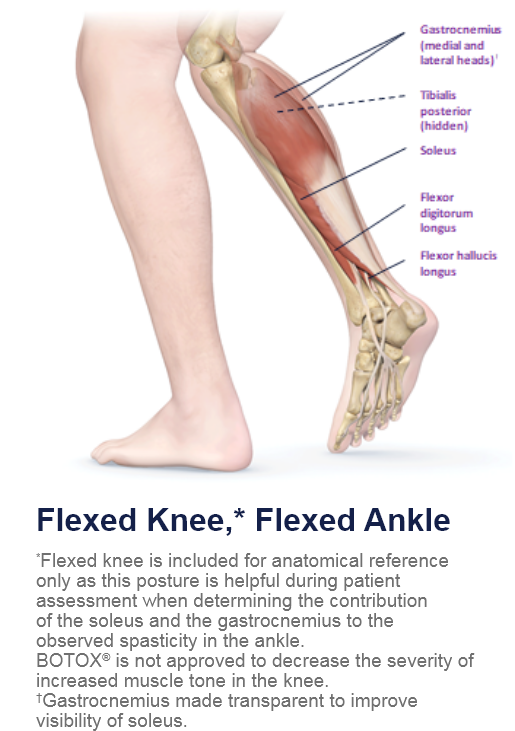
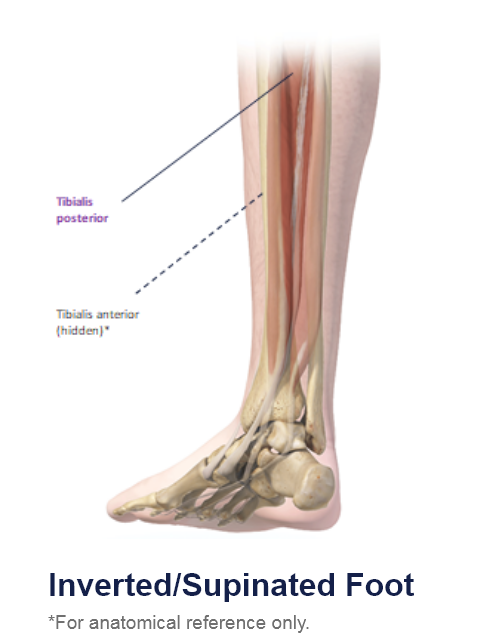
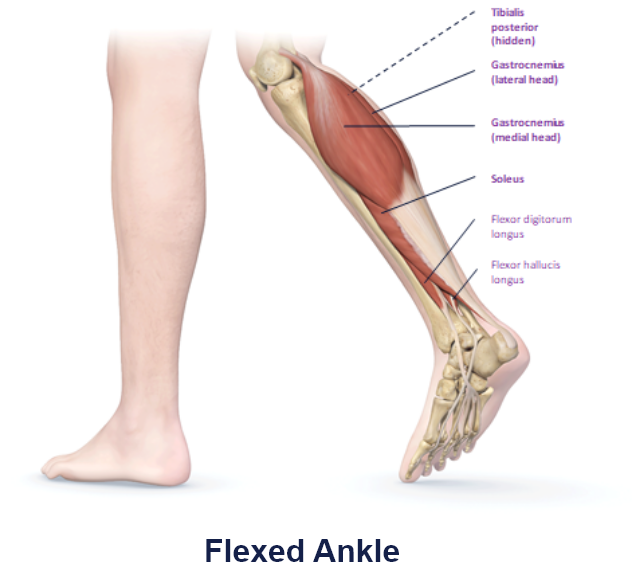
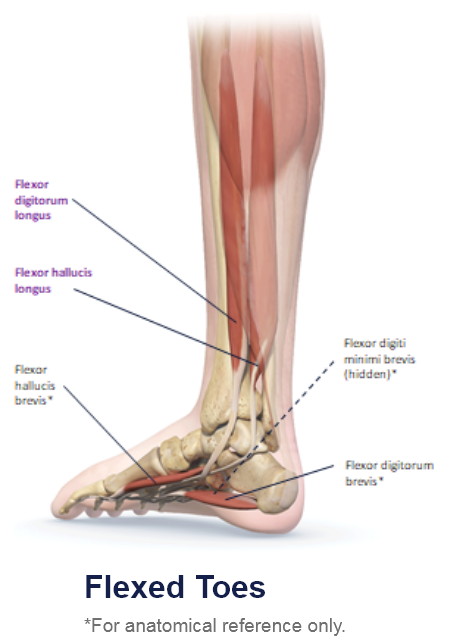
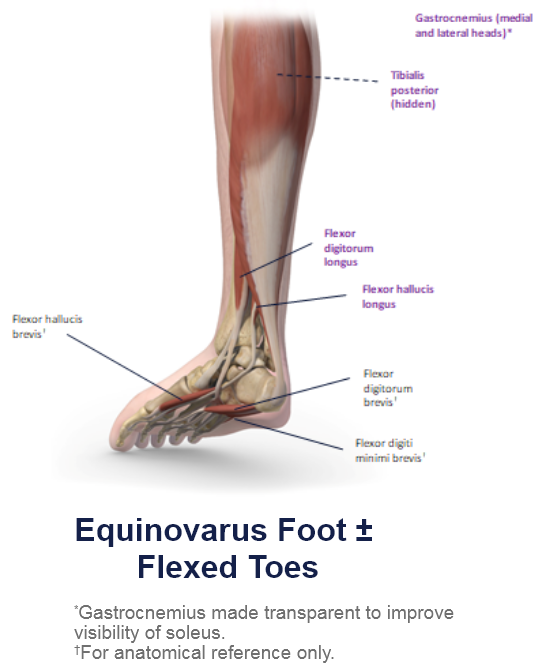
Clinical Presentation Pattern and Associated Muscles
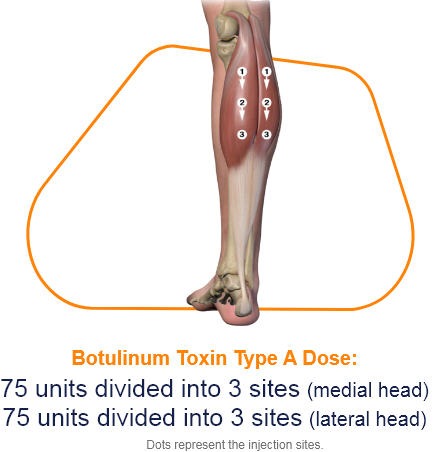
Injection Sites
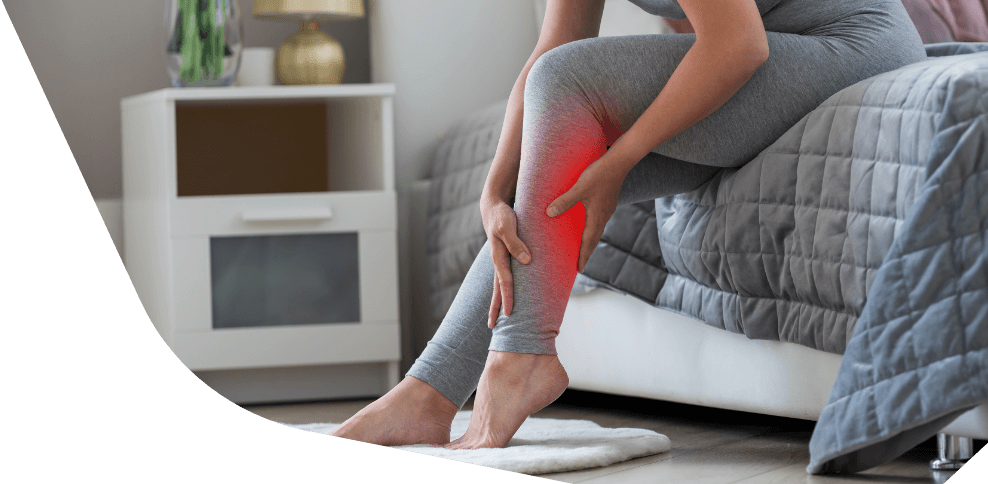
Patterns and Clinical Presentations
The gastrocnemius muscle is one of the calf muscles (triceps surae) in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, which sits superficial to the much larger soleus muscle. It gives the calf its distinctive twoheaded appearance and is a primary plantar flexor.
Its medial border of the lateral head and its lateral border of the medial head forms the inferolateral and inferomedial borders of the popliteal fossa respectively.1
• Function: Plantar flexes the foot and flexes the knee.1
• Origin:
Medial Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the medial femoral condyle.1
Lateral Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the lateral femoral condyle.1
• Insertion: Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon into mid-posterior calcaneus.1
• Innervation: Tibial nerve.2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
The gastrocnemius muscle is one of the calf muscles (triceps surae) in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, which sits superficial to the much larger soleus muscle. It gives the calf its distinctive twoheaded appearance and is a primary plantar flexor.
Its medial border of the lateral head and its lateral border of the medial head forms the inferolateral and inferomedial borders of the popliteal fossa respectively.1
• Function: Plantar flexes the foot and flexes the knee.1
• Origin:
Medial Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the medial femoral condyle.1
Lateral Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the lateral femoral condyle.1
• Insertion: Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon into mid-posterior calcaneus.1
• Innervation: Tibial nerve.2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
The gastrocnemius muscle is one of the calf muscles (triceps surae) in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, which sits superficial to the much larger soleus muscle. It gives the calf its distinctive twoheaded appearance and is a primary plantar flexor.
Its medial border of the lateral head and its lateral border of the medial head forms the inferolateral and inferomedial borders of the popliteal fossa respectively.1
• Function: Plantar flexes the foot and flexes the knee.1
• Origin:
Medial Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the medial femoral condyle.1
Lateral Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the lateral femoral condyle.1
• Insertion: Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon into mid-posterior calcaneus.1
• Innervation: Tibial nerve.2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
The gastrocnemius muscle is one of the calf muscles (triceps surae) in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, which sits superficial to the much larger soleus muscle. It gives the calf its distinctive twoheaded appearance and is a primary plantar flexor.
Its medial border of the lateral head and its lateral border of the medial head forms the inferolateral and inferomedial borders of the popliteal fossa respectively.1
• Function: Plantar flexes the foot and flexes the knee.1
• Origin:
Medial Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the medial femoral condyle.1
Lateral Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the lateral femoral condyle.1
• Insertion: Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon into mid-posterior calcaneus.1
• Innervation: Tibial nerve.2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
The gastrocnemius muscle is one of the calf muscles (triceps surae) in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, which sits superficial to the much larger soleus muscle. It gives the calf its distinctive twoheaded appearance and is a primary plantar flexor.
Its medial border of the lateral head and its lateral border of the medial head forms the inferolateral and inferomedial borders of the popliteal fossa respectively.1
• Function: Plantar flexes the foot and flexes the knee.1
• Origin:
Medial Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the medial femoral condyle.1
Lateral Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the lateral femoral condyle.1
• Insertion: Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon into mid-posterior calcaneus.1
• Innervation: Tibial nerve.2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
The gastrocnemius muscle is one of the calf muscles (triceps surae) in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, which sits superficial to the much larger soleus muscle. It gives the calf its distinctive twoheaded appearance and is a primary plantar flexor.
Its medial border of the lateral head and its lateral border of the medial head forms the inferolateral and inferomedial borders of the popliteal fossa respectively.1
• Function: Plantar flexes the foot and flexes the knee.1
• Origin:
Medial Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the medial femoral condyle.1
Lateral Head: Posterior non-articular surface of the lateral femoral condyle.1
• Insertion: Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon into mid-posterior calcaneus.1
• Innervation: Tibial nerve.2
.
Muscle Function Animation
.
.
Cadaver Demonstration
.
References
1. Radiopaedia.org. (2022). Gastrocnemius muscle. Radiopaedia.org. Last Updated: 6 Feb 2022. Available at: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/gastrocnemius-muscle [Accessed 3 September 2023].
2. Card, R.K. and Bordoni, B., (2019). Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Foot Muscles.
3. Radiopaedia.org. (2021). Soleus muscle. Radiopaedia.org. Last Updated: 16 Nov 2021. Available at: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/soleus-muscle [Accessed 3 September 2023].
4. Corcoran, N.M. and Varacallo, M., (2021). Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Tibialis Posterior Muscle. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
5. Jones J, Al Kabbani A, Hacking C, et al. (2009). Tibialis posterior muscle. Radiopaedia. Last Updated: 1 August 2022. Available at: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/tibialis-posterior-muscle [Accessed 2 August 2023].
6. Mitchell, Adam & drake, & Vogl, A.. (2015). Gray's Anatomy for Students, 3rd Edition.
7. Mostafa, E., Graefe, S.B. and Varacallo, M. (2022). Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Leg Posterior Compartment. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
8. Radiopaedia.org. (2021). Flexor digitorum brevis muscle. Radiopaedia.org. Last Updated: 3 Aug 2021. Available at: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/flexor-digitorum-brevis-muscle [Accessed 3 September 2023].