The efficacy and safety of 24-hour continuous levodopa-based therapy with VYALEV™ were demonstrated in 2 trials.1-3
IR=immediate-release.
Aim: Evaluate the efficacy and safety of VYALEV™ to oral IR levodopa/carbidopa in patients with advanced PD.
Duration: 12 weeks.
Study type: Phase 3, 1:1 randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled.
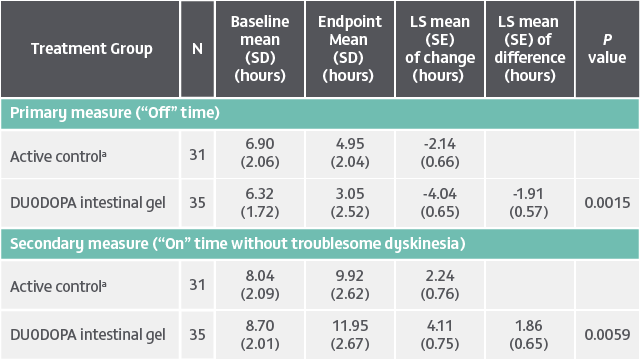
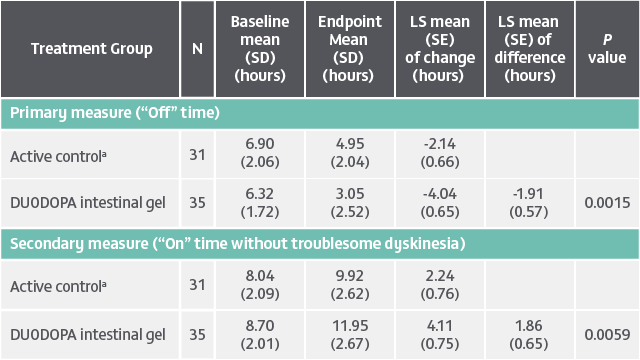
Patient population: Evaluation of 141 patients. The target population was levodopa-responsive patients with advanced PD whose motor symptoms were inadequately controlled with current treatment and experienced minimum daily average of 2.5 hours of “Off” time per day, as assessed by PD diaries.*
Of the 74 patients receiving VYALEV™, 48 completed the study and 26 discontinued treatment.
Of the 67 patients receiving optimized oral IR levodopa/carbidopa, 62 completed treatment and 5 discontinued.
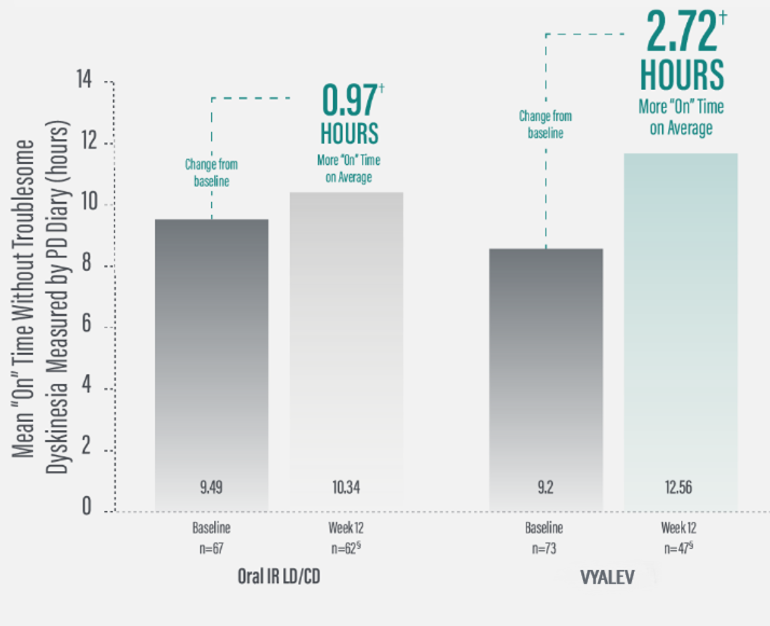
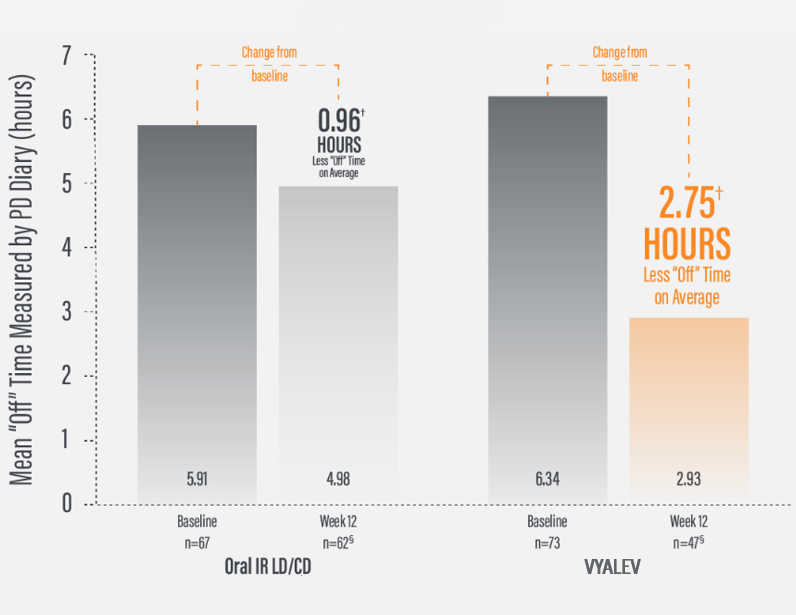
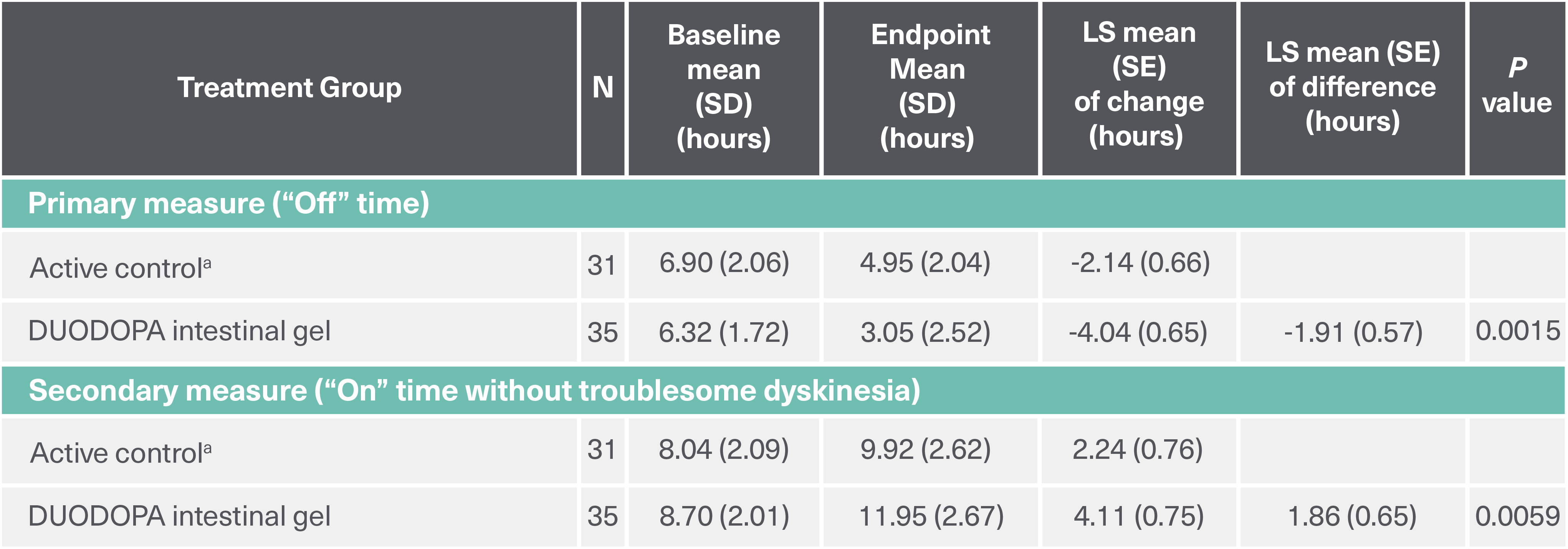
*Based on the PD diary, the average daily normalized “On” time for patients on VYALEV™ was 9.20 (+/−2.42) hours at baseline and increased by 2.72 (+/−0.52) hours at Week 12 compared with an increase of 0.97 (+/−0.50) hours at Week 12 from a baseline of 9.49 (+/−2.62) hours for patients taking optimized oral IR LD/CD. This resulted in a statistically significant increase of 1.75 (+/−0.65) hours in daily normalized “On” time without troublesome dyskinesia in patients on VYALEV™ vs oral IR LD/CD (LS mean of difference [SE]; P=0.0083). Average daily normalized “Off” time for patients on VYALEV™ was 6.34 (+/−2.27) hours at baseline and decreased by 2.75 (+/−0.50) hours at Week 12 compared with a decrease of 0.96 (+/−0.49) hours at Week 12 from a baseline of 5.91 (+/−1.88) hours for patients taking optimized oral IR LD/CD (LS mean change [SE]). This resulted in a statistically significant reduction of 1.79 (+/−0.63) hours in “Off” time in patients on VYALEV™ vs oral IR LD/CD (LS mean of difference [SE]; P=0.0054).
CI=confidence interval; IR=immediate-release; LD/CD=levodopa/carbidopa; PD=Parkinson’s disease; LS=least squares.
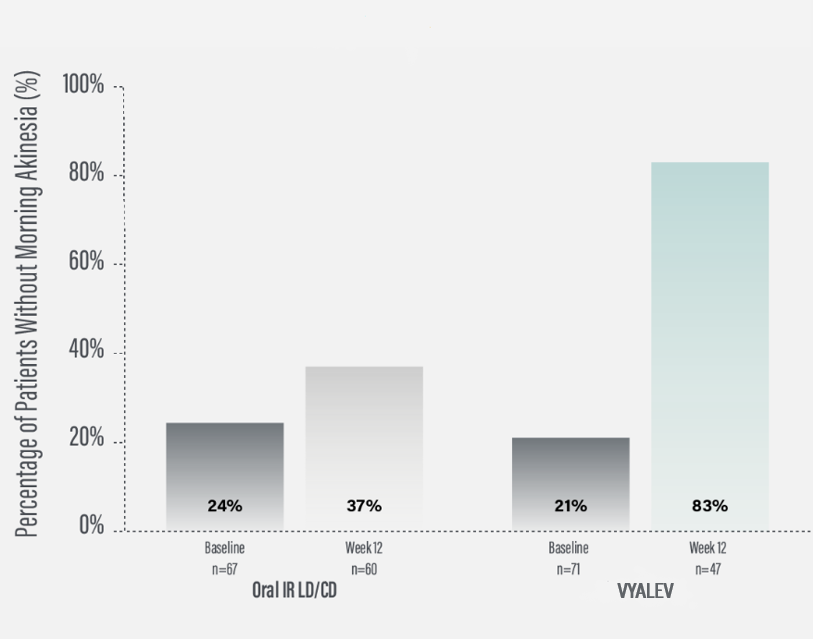
*As demonstrated by a reduction in the number of patients reporting morning “Off” (morning akinesia) in their PD diaries from baseline to Week 52. Morning akinesia was defined as reporting “Off” status as the first morning symptom upon awakening.3
†In the clinical trials, patients recorded their PD symptoms in a PD diary, which was completed for a full 24-hour period. Patients made an entry upon waking and every 30 minutes during their normal waking time. Patients recorded whether they were “On,” “Off,” or “Asleep” and what the severity of their dyskinesia (troublesome or not troublesome) was.3
‡More refers to “On” time compared to oral IR levodopa/carbidopa. Patients in the VYALEV™ study experienced significant improvements compared with oral IR levodopa/carbidopa at Week 12, including “On” time without troublesome dyskinesia and “Off” time.3
IR=immediate-release; PD=Parkinson’s disease.
(LS mean of difference between the two treatment arms=1.75 hours; P=0.0083 [95% CI, 0.46, 3.05])
*Based on the PD diary, the average daily normalized “On” time without troublesome dyskinesia for patients on VYALEV™ was 9.20 (+/-2.42) hours at baseline and increased by 2.72 (+/-0.52) hours at Week 12 compared with an increase of 0.97 (+/-0.50) hours at Week 12 from a baseline of 9.49 (+/-2.62) hours for patients taking optimized oral IR levodopa/carbidopa (LS mean change [SE]). This resulted in a statistically significant increase of 1.75 (+/-0.65) hours in patients on VYALEV™ vs oral IR LD/CD (LS mean of difference [SE]; P=0.0083). “On” time without troublesome dyskinesia/good “On” time is the sum of “On” time without dyskinesia and “On” time with non-troublesome dyskinesia.
†Model-based least square mean (standard error) of change.
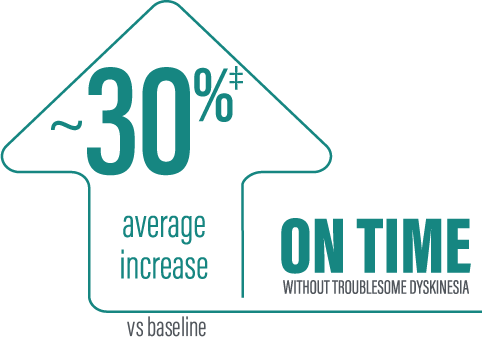
‡Calculated by dividing the change in hours from baseline by the number of hours reported at baseline ([2.72/9.2] x 100 = 29.57%).
§A total of 110 patients (oral IR LD/CD n=62; VYALEV™ n=48) completed the study. During the double-blind treatment period, 5 patients in the oral IR LD/CD group and 26 in the VYALEV™ group prematurely discontinued. One of the patients in the VYALEV™ group was excluded from the analysis because the patient did not have valid baseline data for the efficacy model.
IR=immediate-release; LD/CD=levodopa/carbidopa; LS=least squares; PD=Parkinson’s disease; SE=standard error.
(LS mean of difference between the two treatment arms=-1.79 hours; P=0.0054 [95% CI, -3.03, -0.54])
*Based on the PD diary, the average daily normalized “Off” time for patients on VYALEV™ was 6.34 (+/-2.27) hours at baseline and decreased by 2.75 (+/-0.50) hours at Week 12 compared with a decrease of 0.96 (+/-0.49) hours at Week 12 from a baseline of 5.91 (+/-1.88) hours for patients taking optimized oral IR levodopa/carbidopa (LS mean change [SE]). This resulted in a statistically significant reduction of 1.79 (+/-0.63) hours in patients on VYALEV™ vs oral IR LD/CD (LS mean of difference [SE]; P=0.0054).
†Model-based least square mean (standard error) of change.
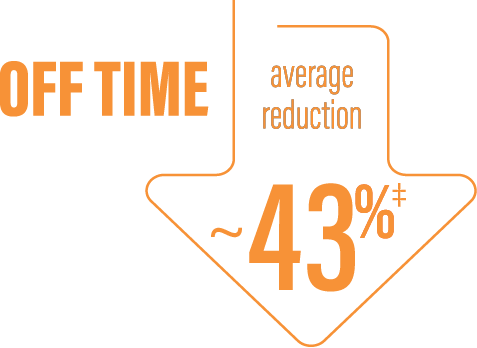
‡Calculated by dividing the change in hours from baseline by the number of hours reported at baseline ([2.75/6.34] x 100 = 43.38%).
§A total of 110 patients (oral IR LD/CD n=62; VYALEV™ n=48) completed the study. During the double-blind treatment period, 5 patients in the oral IR LD/CD group and 26 in the VYALEV™ group prematurely discontinued. One of the patients in the VYALEV™ group was excluded from the analysis because the patient did not have valid baseline data for the efficacy model.
CI=confidence interval; IR=immediate-release; LD/CD=levodopa/carbidopa; LS=least squares; PD=Parkinson’s disease; SD=standard deviation.
*Morning akinesia was defined as reporting “Off” status as the first morning symptom upon awakening.
†Percentage of patients without morning akinesia is the sum of patients reporting “On” time without dyskinesia, “On” time with non-troublesome dyskinesia, and “On” time with troublesome dyskinesia upon awakening.
‡For patients on VYALEV™, based on PD diary, “On” time without dyskinesia was reported in 70% (N=33/47) of patients; “On” with non-troublesome dyskinesia in 8% (N=4/47) of patients; “On” with troublesome dyskinesia was reported in 4% (N=2/47) of patients at Week 12. For patients on oral IR LD/CD, based on the PD diary, “On” time without dyskinesia was reported in 37% (N=22/66) of patients at Week 12. For patients on VYALEV™, based on the PD diary, morning akinesia was reported in 79% (N=56/71) of patients at baseline and in 17% (N=8/47) of patients at Week 12. For patients on oral IR LD/CD, based on the PD diary, morning akinesia was reported in 76% (N=51/67) of patients at baseline and in 63% (N=38/60) of patients at Week 12.
IR=immediate-release; LD/CD=levodopa/carbidopa; PD=Parkinson’s disease.
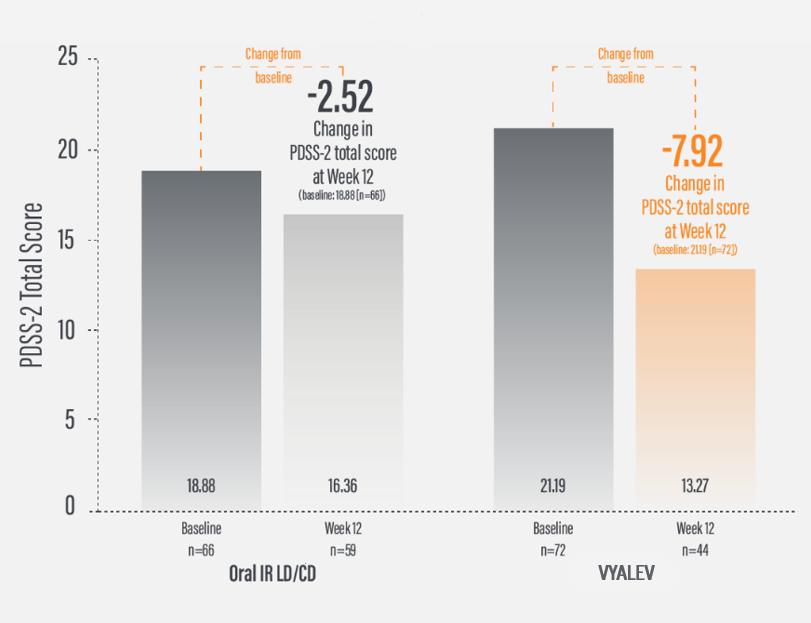
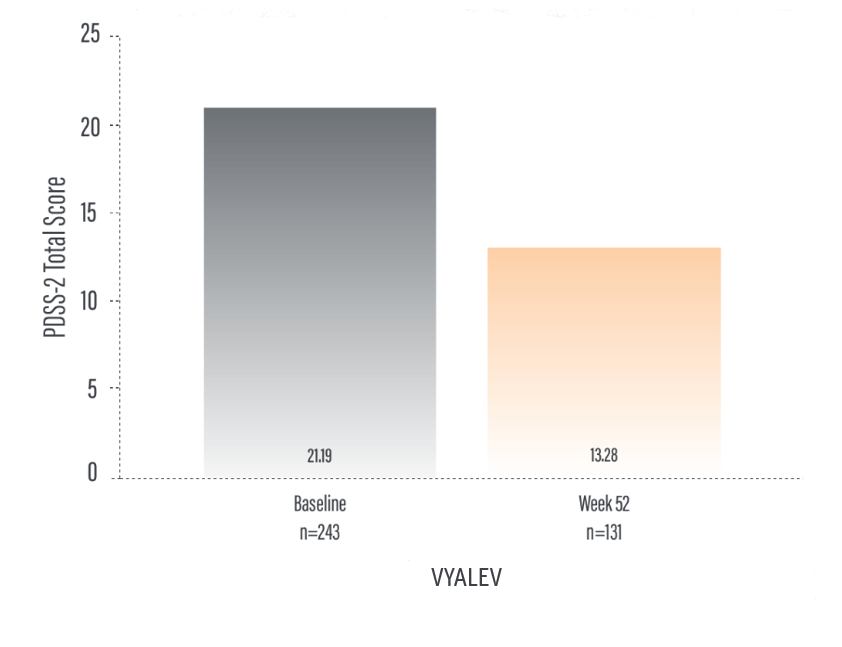
*For patients on VYALEV™, the PDSS-2 total score was 21.19 (n=72) at baseline with a change of -7.92 (n=44) at Week 12. For patients on oral IR LD/CD the PDSS-2 total score was 18.88 (n=66) at baseline with a change of -2.52 (n=59) at Week 12.
†Calculated by dividing the change in score from baseline by the score reported at baseline.
IR=immediate-release; LD/CD=levodopa/carbidopa; PDSS-2=Parkinson’s Disease Sleep Scale-2.
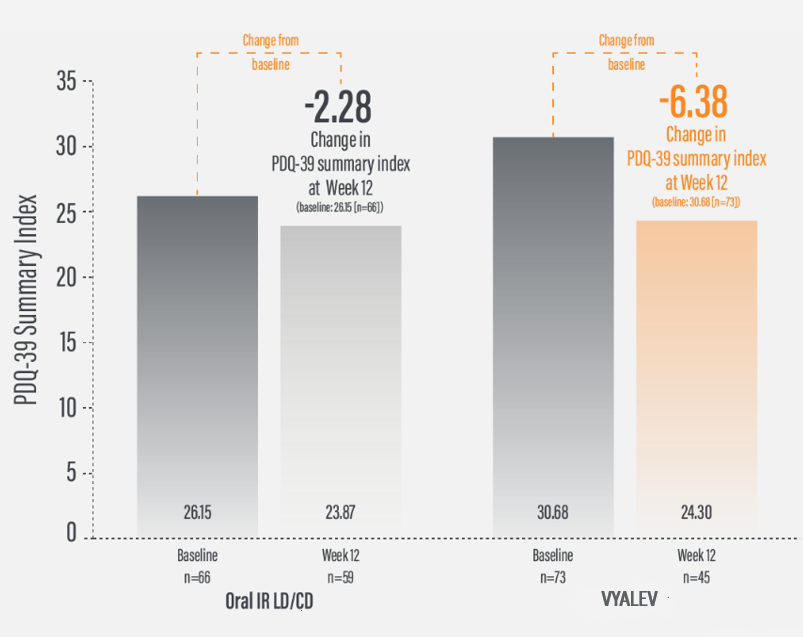
*For patients on VYALEV™, the mean (SD) PDQ-39 summary index value was 30.68 (n=73) at baseline with a change of -6.38 (n=45) at Week 12. For patients on oral IR LD/CD the mean (SD) PDQ-39 summary index value was 26.15 (n=66) at baseline with a change of -2.28 (n=59) at Week 12.
†Calculated by dividing the change in score from baseline by the score reported at baseline.
IR=immediate-release; LD/CD=levodopa/carbidopa; PDQ-39=39-item Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire; QoL=quality of life; SD=standard deviation.
Aim: Evaluate the safety and tolerability of 24-hour daily exposure with a continuous subcutaneous infusion of VYALEV™. Secondary efficacy endpoints were also evaluated.
Duration: 52 weeks (this study is ongoing).
Study type: Phase 3, single-arm, open-label.
Patient population: Evaluation of 244 patients. 137 patients completed the 52-week study. The target population was levodopa-responsive patients with PD whose motor symptoms were inadequately controlled with current treatment and experienced a minimum of 2.5 hours of “Off” time per day as assessed by PD diaries.
PD=Parkinson’s disease.
*"On" time without troublesome dyskinesia is the sum of "On" time without dyskinesia and "On" time with non-troublesome dyskinesia.
†Values represent unadjusted mean hours (+/-standard deviation) assessed using a 24-hour PD diary and normalized to a 16-hour waking day. Only patients who completed each study visit were included in the efficacy analysis, and no adjustments were made to account for premature discontinuation.
‡52-week value is the sum of 10.8 hours ("On" time without dyskinesia) and 2.3 hours ("On" time with non-troublesome dyskinesia).
§Calculated by dividing the change in hours from baseline by the number of hours reported at baseline.
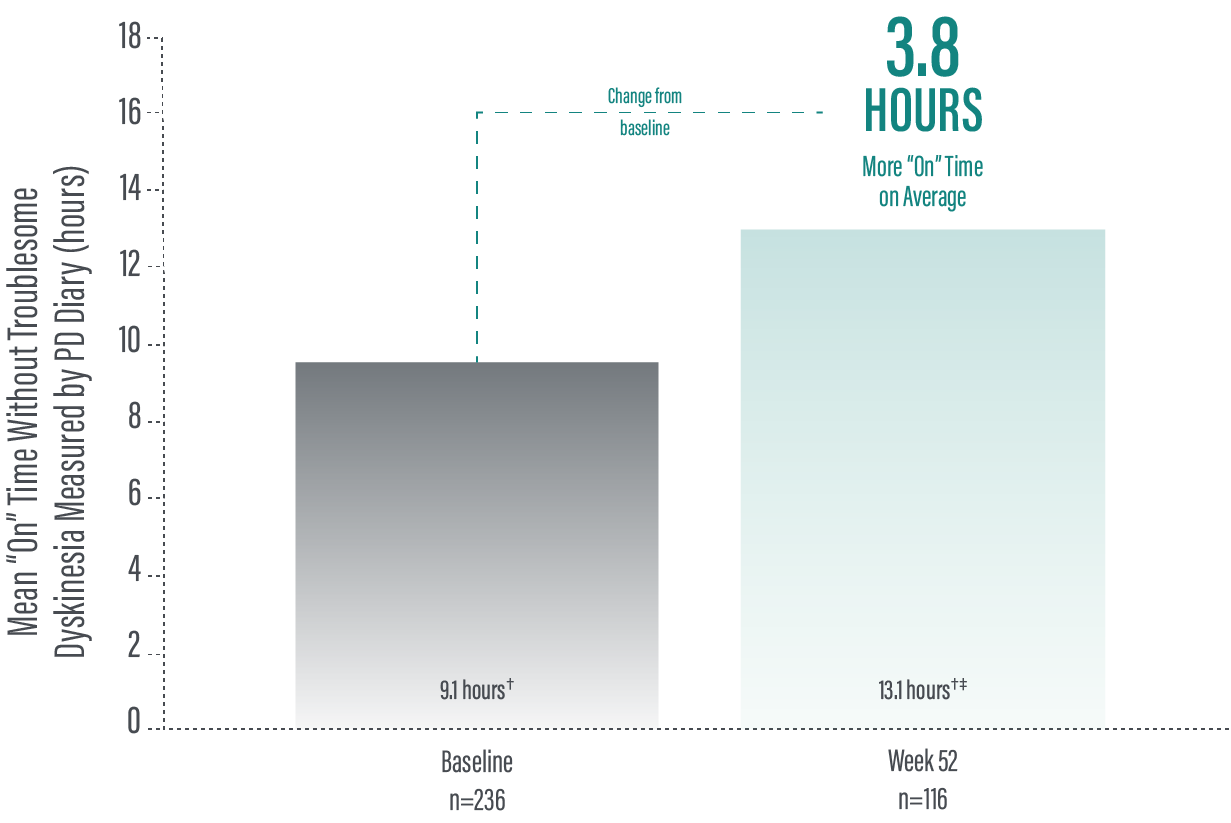
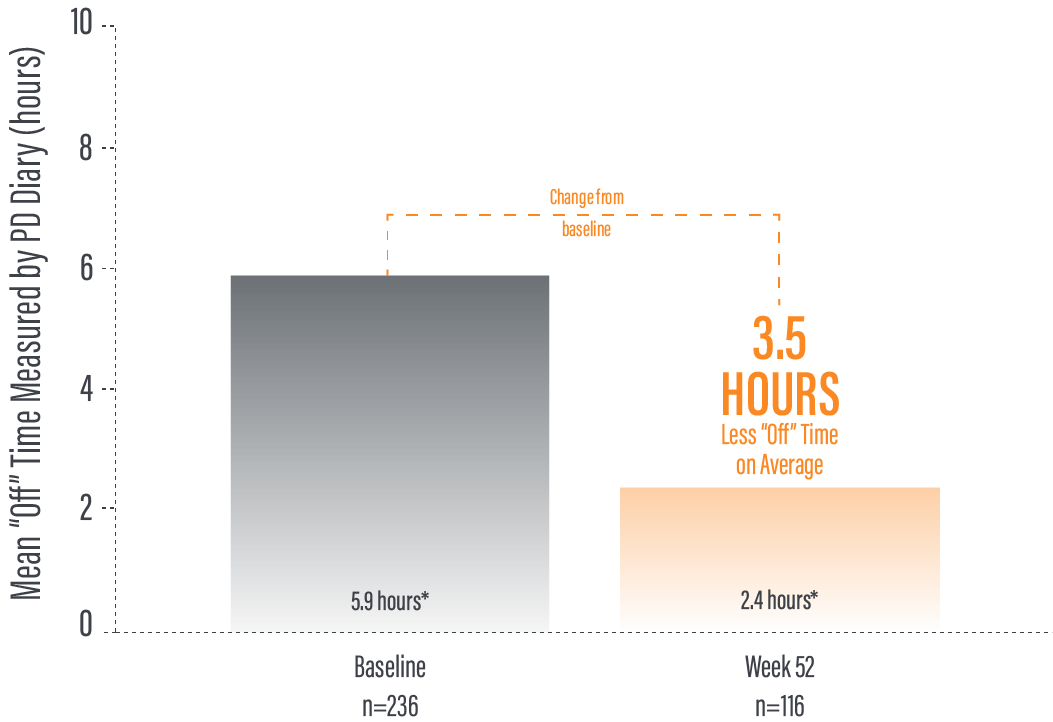
*“Off” time was decreased by an average of 3.5 hours by Week 52 (average 2.5 hours) compared to baseline (average 5.9 hours) as demonstrated by a the average daily normalized “Off” time for patients in their PD diaries from baseline to study end (n=116).2
†Calculated by dividing the change in hours from baseline by the number of hours reported at baseline.
Continue to Safety page
Please refer to the VYALEV™ SmPC for complete Prescribing and Safety Infomation.