This promotional material is intended for UK Healthcare Professionals (HCPs) experienced in the diagnosis and management of Parkinson’s disease only. Adverse event reporting can be found below
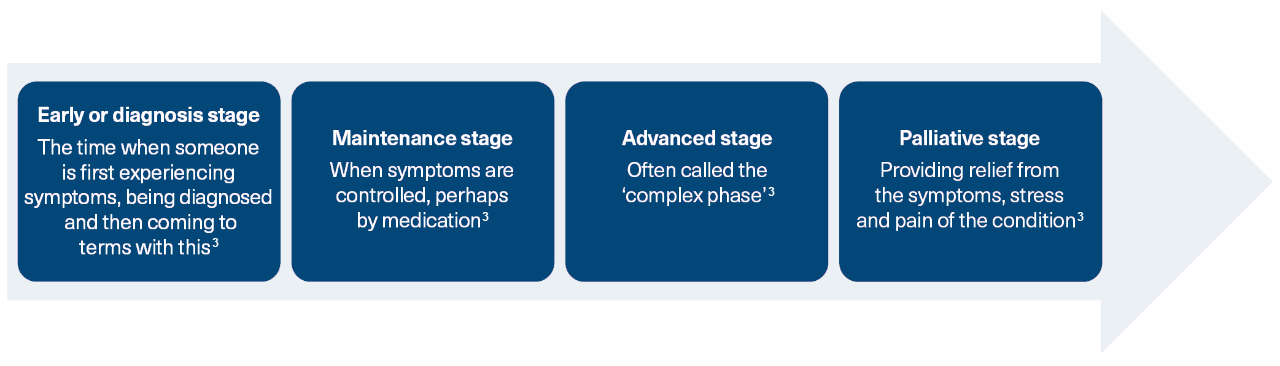
The progressive stages of Parkinson’s
Pinpointing the progression of a patient’s Parkinson’s disease (PD) to a more Complex/Advanced stage is difficult, but a key indicator is when symptoms become more complex and start affecting daily life.3 As their condition advances, people with PD commonly develop motor response fluctuations and/or dyskinesias.4,5
Learn more about patient burden
Stay connected
Keep up to date with future resources, support, and guidance to help you manage your patients with PD by filling out your details below and joining the mailing list.
Please only fill out your details if you are a UK registered healthcare professional.
1. DUODOPA (levodopa/carbidopa intestinal gel) SmPC.
2. PRODUODOPA (foslevodopa/foscarbidopa solution for infusion) SmPC.
3. Parkinson’s UK. Advanced Parkinson’s. Available at: https://www.parkinsons.org.uk/information-and-support/advanced-parkinsons. Accessed December 2024.
4. Odin P, et al. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2015; 21: 1133–44.
5. Worth PF. Pract Neurol 2013; 13: 140–52.
6. Antonini A, et al. Curr Med Res Opin. 2018; 34: 2063–73.
7. Nyholm D. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2007; 13 Suppl: S13–7.
8. Olanow CW, et al. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2006; 2(7): 382–92.
9.Varanese S, et al. Parkinsons Dis. 2011; 2010: 480260.
10. Fleisher JE, Stern MB. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2013; 13(10): 382.
11. Grosset KA, et al. Mov Disord. 2005; 20(11): 1502–7.
By clicking the links above you will leave the AbbVie Pro website and be taken to the eMC PI portal website
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at yellowcard.mhra.gov.uk or via the MHRA Yellow Card app, available in the Google Play or Apple App Stores.
Adverse events should also be reported to AbbVie on GBPV@abbvie.com
UK-PRODD-240194. Date of preparation: December 2024