Recommendations for specialist headache clinics and service provision
The content below is extracted from the NHS Getting It Right First Time review of neurology.6
The full report can be accessed here
GIRFT recommends that specialist clinics be established locally with the correct capacity and frequency to reflect the local need, with specialist clinics for the most common neurological disorders to be available at all but the smallest sites.
The specialist overseeing the clinic need not be based at that specific site.
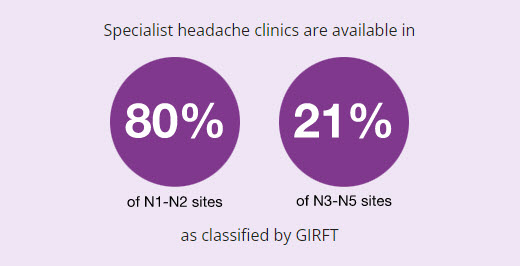
GIRFT Recommendation 9
Establish specialist clinics for the most common neurological disorders locally at all sites, with network links to regional or national services
(a) Establish specialist treatment clinics to provide special injection services or other minor procedures†
†Including BOTOX® injection for chronic migraine.
Patients with chronic neurological disorders should have access to appropriate specialist nurses or advanced practitioners, irrespective of their geographical location. However, only 25 specialist headache nurses were reported to GIRFT across England, 16 of whom were based at N1 sites.
GIRFT Recommendation 10
Ensure that patients with chronic neurological disorders have access to specialist nurses or other advanced practitioners working as part of an integrated multidisciplinary team, with appropriate administrative support.
(a) Integrate specialist nursing and advanced practitioner resource within the neurology service to enhance and maintain specialist skills
(b) Develop credential proposals for consideration by Health Education England, with a view to standardising training for advanced practitioners (including specialist nurses) and covering both general neurology and disease‑specific support.
Management of severe migraine such as chronic migraine is changing with the introduction of treatments such as BOTOX® and anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies.
There is geographical variation in the provision of BOTOX®. It is available at most neuroscience and neurology centres, and is typically administered by a consultant neurologist or a headache specialist nurse.
GIRFT recommends that BOTOX® clinics for headache should be available locally to patients, and should make use of all appropriately qualified healthcare practitioners.
GIRFT Recommendation 18
Review and improve local provision of treatments for chronic neurological conditions to ensure patients can access care as close to home as possible
(b) Review pathways to ensure that BOTOX® clinics for chronic migraine are available at sites close to patients’ homes.
Where possible, appropriately qualified healthcare practitioners should be trained to provide BOTOX® injections for those patients with stable treatments, with appropriate clinical governance
CGRP: calcitonin gene-related peptide; CM: chronic migraine.
Please refer to the BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics for further information on adverse events, contraindications and special warnings and precautions for use.
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at https://yellowcard.mhra.gov.uk
Adverse events should also be reported to AbbVie on GBPV@abbvie.com
Date of preparation: March 2024. UK-BCM-240049.