BOTOX® has demonstrated efficacy in post‑stroke spasticity (PSS) in both the upper and lower limb5-9
BOTOX® has demonstrated efficacy in upper limb PSS6
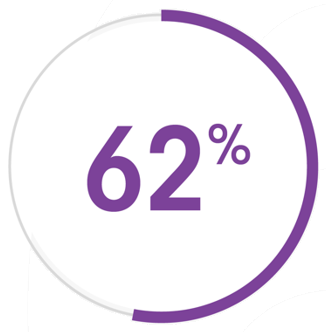
BOTOX® helped significantly more patients achieve upper limb functional goals vs placebo6
Primary endpoint: Functional disability was measured using the four-point Disability Assessment Scale (hygiene, dressing, pain and limb position) at week 66
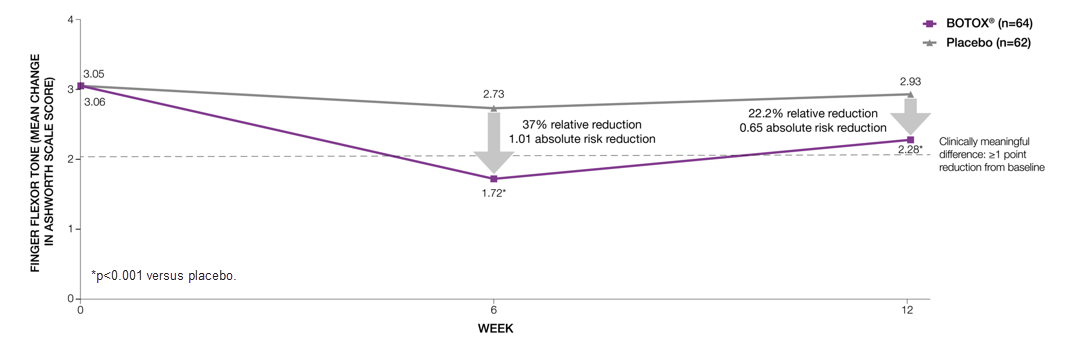
BOTOX® significantly reduced finger flexor tone compared to placebo at both Week 6 (primary endpoint) and 12 (additional endpoint)6
Adapted from Brashear A, et al 2002.6
Study context: A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial assessed the efficacy and safety of BOTOX® in 126 subjects with increased flexor tone in the wrist and fingers after a stroke6.
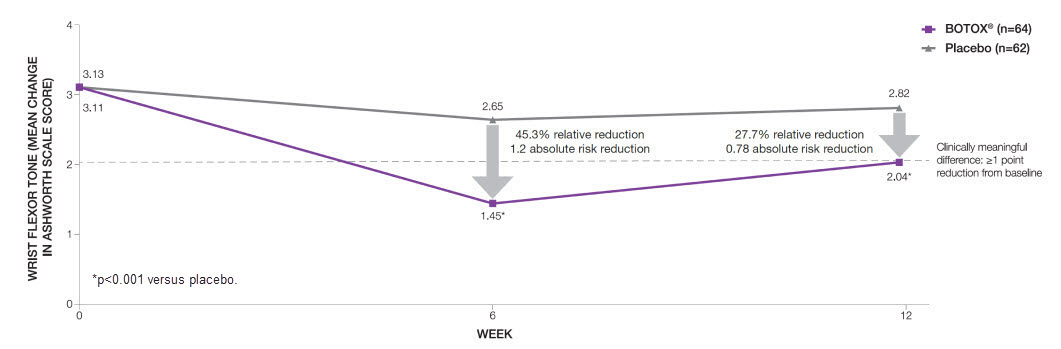
BOTOX® significantly* reduced wrist flexor tone compared to placebo at both Week 6 (primary endpoint) and 12 (additional endpoint)6
Adapted from Brashear A, et al 2002.6
Study context: A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial assessed the efficacy and safety of BOTOX® in 126 subjects with increased flexor tone in the wrist and fingers after a stroke.6
BOTOX® has demonstrated efficacy in upper limb PSS6
BOTOX® helped significantly more patients achieve upper limb functional goals vs placebo6
Primary endpoint: Functional disability was measured using the four-point Disability Assessment Scale (hygiene, dressing, pain and limb position) at week 66
BOTOX® significantly reduced finger flexor tone compared to placebo at both Week 6 (primary endpoint) and 12 (additional endpoint)6
Adapted from Brashear A, et al 2002.6
Study context: A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial assessed the efficacy and safety of BOTOX® in 126 subjects with increased flexor tone in the wrist and fingers after a stroke6.
BOTOX® significantly* reduced wrist flexor tone compared to placebo at both Week 6 (primary endpoint) and 12 (additional endpoint)6
Adapted from Brashear A, et al 2002.6
Study context: A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial assessed the efficacy and safety of BOTOX® in 126 subjects with increased flexor tone in the wrist and fingers after a stroke.6
AUC, area under curve; MAS, Modified Ashworth Scale; PSLLS, post-stroke lower limb spasticity; PSS, post-stroke spasticity.
Please refer to the BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics for further information on adverse events, contraindications and special warnings and precautions for use. The BOTOX® Summary of Product Characteristics can be found here
By clicking the link above you will leave the AbbVie Pro website and be taken to the eMC PI portal website.
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at https://yellowcard.mhra.gov.uk/ or via the MHRA Yellow Card app, available in the Google Play or Apple App Stores.
Adverse events should also be reported to AbbVie on GBPV@abbvie.com
Date of preparation: June 2025. UK-BTX-250065.